* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture04
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
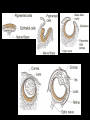
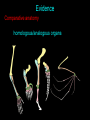
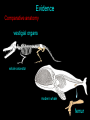
Arguments & evidence How incredibly stupid not to have thought of that Thomas Huxley Arguments Blending inheritance Variability Isolation Age of the earth Arguments Blending inheritance -new adaptations diluted with each generation Darwin’s reply: Favorable traits maintained if popln isolated Some traits ‘preponent’ Adaptive traits arise often Enhanced reproduction of favorable traits Arguments Variability -Darwin confined natural selection to small, continuous variation How could new spp arise from small variations? -successive change through time How could small variations confer an advantage? -Darwin could not answer, later demonstrated How could selection act on a nonexistent trait? -preadaptation - new organ modified from another 1% per generation change in anatomy <500000 yrs Arguments Isolation -how could a new spp evolve in close proximity to its parents Darwin did not emphasize isolation as a primary cause for evolution Arguments Age of the earth -earth was not old enough to allow time for evolution Biblical 5,000 Newton 50,000 Buffon 75,000 Kelvin 100,000,000 present 4,500,000,000 Arguments Blending inheritance Variability Isolation Age of the earth Evidence Systematics Geographic distribution Comparative anatomy Embryology Fossils Artificial selection Direct observation Evidence Systematics -gradation of species easily understood by evolutionary relationships Evidence Geographic distribution -evolutionarily related organisms geographically connected Evidence Geographic distribution -evolutionarily related organisms geographically connected marsupial radiation Evidence Comparative anatomy homologous/analogous organs Evidence Comparative anatomy homologous/analogous organs Darwin’s interpretation of homology has become the definition: similarity due to common ancestry Evidence Comparative anatomy homologous/analogous organs Organisms show curious similarities in structure and development unrelated to function Evidence Comparative anatomy convergent evolution Evidence Comparative anatomy vestigial organs Evidence Comparative anatomy vestigial organs whale ancestor modern whale femur Organisms have vestigial structural, developmental and molecular traits Vestigial structures are a manifestation of change through time Evidence Embryology -remarkable similarity among diverse vertebrates Evidence Fossils -vast majority of fossil forms differ from extant spp extinction succession transitional forms environmental changes Evidence Fossils -vast majority of fossil forms differ from extant spp extinction The fact that many species have gone extinct suggests that Earth’s flora and fauna have changed over time Evidence Fossils -vast majority of fossil forms differ from extant spp transitional forms Evidence Fossils -vast majority of fossil forms differ from extant spp “living fossils” Evidence Fossils -vast majority of fossil forms differ from extant spp extinction succession transitional forms environmental changes Evidence Artificial selection -accelerated evolution based on human-favored traits Evidence Artificial selection -accelerated evolution based on human-favored traits Evidence Direct observation -natural selection can be observed in real time Observations on living organisms show that populations and species change over time