* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
On the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
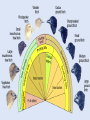
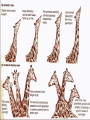
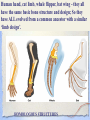
Theory of Natural Selection: Darwin’s explanation for HOW evolution works. VOYAGE OF THE HMS BEAGLE : 1831 - 1836 7 Steps to Natural Selection 4. Struggle for existence- 1. Overpopulation competition for water, food, & (overproduction)shelter animals produce more of the fittest- the offspring than survive. 5. Survival best adapted & strongest tend to survive longer & produce 2. Variation- animals of more offspring the same species are 6. Inheritance- favored/best different fit/selected variations 3. Change in (characteristics) are passed on to offspring. environment7. New species arise- “selected” a) Biological - food, individuals grow in number predators, shelter, etc. and become a new species that cannot reproduce with b) Physical…water, original species oxygen, temp, etc. Darwin’s Observation: 13 or so species of finches on different Galapagos islands; these finches resembled the South American (mainland) finches more than say finches in Asia…. Same process for other species! Jean Baptiste Lamarck: the outcaste! used the fossil record as evidence proposed a theory of evolution where organisms became better and better Mechanism - ”use” and “disuse” leads to: inheritance of acquired characteristics (you ‘acquire’ a phenotype in your lifetime and pass it on to your kids) also means environmental influences can be inherited DON’T BE LAMARCKIAN! Hugo DeVries & Mutation Theory • New Characteristics suddenly appear – Mutation • These can be passed on and may or may not help a species become more fit • Helped to modify Darwin’s Theory Evidences for Darwin’s theory • • • • Fossil record - horse lab Homologous Structures Vestigial structures Artificial selection • Natural selection in action: the evolution of insecticide-resistance occurs in nature - individuals with the best fit genes that can resist the insecticide will survive…. Fig. 22.12 B) HOMOLOGIES – • Similarities in characteristics resulting from common ancestry is known as homology. • 1) Homologous Structures: Same skeletal elements, but different functions Human hand, cat limb, whale flipper, bat wing - they all have the same basic bone structure and design; So they have ALL evolved a common ancestor with B)from HOMOLOGIES – a similar ‘limb design’. HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES C) Vestigial organs, structures that are not used, but which had important functions in ancestors still retained in descendents, so evolution/change has occurred. Some Alleged Vestigial Organs in Man Tonsils Coccyx (tail bone) Thymus Little toe Nipples on males Nodes on ears "Darwin's points" Pineal gland Adenoids Nictitating membrane of eye Appendix Wisdom teeth Parathyroid Ear muscles for wiggling Body hair C) Vestigial organs – spurs in snakes, hind leg bones in whales. Artificial Selection • Artificial Selection: The selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to encourage the occurrence of desirable traits. • Short period of time needed for Artificial Selection Heredity: Characteristics that are passed down to offspring Mutations: Changes that occur in the hereditary material Mutant: The new form that survives a mutation and passes this trait on to offspring Adaptation: A favorable variation within a species that may help an organism survive • Natural selection Predators/famine/space shortage/disease/ environmental changes Origin of life and Stanley Miller’s Experiment Abiotic synthesis of organic monomers • Stanely Miller - simulated conditions on early Earth (no oxygen, reducing environment with inorganic gases like H2, CO2, NH3, CH4; lightning/UV with no ozone. Favored the synthesis of organic compounds from inorganicmaterial The Miller-Urey experiments produced a variety of amino acids and other organic molecules (monomers).