* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolutionary trends - Life is a journey: Mr. T finding his way
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
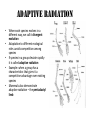
Evolutionary trends By Martin Samaj Rates of evolution • Gradualism – claims that evolution proceeds very slowly, large changes can occur over long periods of time • This theory does not fit with fossil record, which show periods where the evolutionary rate was stable, followed by a period of rapid changes • These changes in evolutionary rates may be due to the environmental changes which would require the species to adapt to these new conditions • This view of the pace of evolution is called punctuated equilibrium Adaptive radiation • When each species evolves in a different way, we call it divergent evolution • Adaptation to different ecological roles avoids competition among species • If species in a group deviate rapidly it is called adaptive radiation • Example: when a group has a characteristics that gives it a competitive advantage over existing species • Mammals also demonstrate adaptive radiation – the pentadactyl limb Transient polymorphism • Population in which there are two alleles of a gene in the gene pool is polymorphic • If one allele is gradually replacing the other the population shows transient polymorphism • The peppered moth is an example of this Convergent evolution • Living organisms often find the same solutions to particular physiological problems • If natural selection acts the same also in other parts of the world, species can become remarkably different despite not being closely related at all • This is called convergent evolution • Instead of closely related species showing striking differences, unrelated species show striking similarities Balanced Polymorphism • Sometimes alleles of gene can persist indefinitely in the gene pool of a population • This is called balanced polymorphism • The most researched example of this would be sickle anemia • Heterozygous individuals do not develop sickle cell anemia and are resistant to sickle cell anemia Danke for paying attention