* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ν e
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Super-Kamiokande wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Wheeler's delayed choice experiment wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Photomultiplier wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
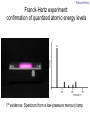
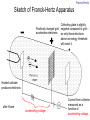
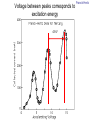
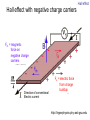
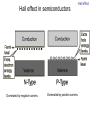
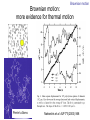
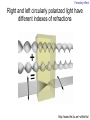
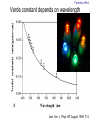
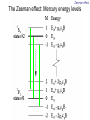
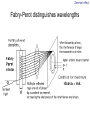
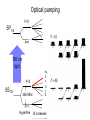
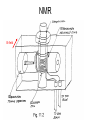
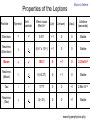
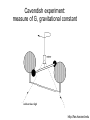
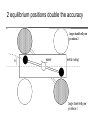
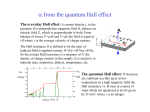
Introduction to the experiments of Physics 407 Franck-Hertz Franck-Hertz experiment: confirmation of quantized atomic energy levels 1st evidence: Spectrum from a low-pressure mercury lamp Franck-Hertz Sketch of Franck-Hertz Apparatus Collecting plate is slightly Positively charged grid negative compared to grid – accelerates electrons so only those electrons above an energy threshold will reach it. + Heated cathode produces electrons after Krane accelerating voltage Current from collector measured as a function of accelerating voltage. Voltage between peaks corresponds to excitation energy 4.9 V Franck-Hertz Hall effect Hall effect with negative charge carriers + Fm = magnetic force on negative charge carriers Direction of conventional Electric current Fe = electric force from charge buildup http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu Hall effect Hall effect in semiconductors Dominated by negative carriers. Dominated by positive carriers. Johnson noise Johnson Noise + Cause: Thermal motion 0 Vrms?? Johnson noise Johnson Noise: way to measure Boltzmann’s constant JB Johnson, Physical Review 32 (1928) 97 Brownian motion Brownian motion: more evidence for thermal motion Perrin’s Atoms Nakroshis et al. AJP 71 (2003) 568 Chaos State space of a dynamical system IDEAL FRICTION James P. Crutchfield, J. Doyne Farmer, Norman H. Packard, and Robert S. Shaw SCIENTIFIC AMERICAN DECEMBER, 1986 VOL. 254 NO. 12, 46-57. Chaos 10,000 red dots Chaos Chaotic behavior is characterized by divergence of nearby trajectories. Lyapunov exponent is a measure of this divergence. 2 slit interference, one photon Two-slit interference one photon at a time: grappling with wave/particle duality Single photon interference: “a phenomenon which is impossible, absolutely impossible to explain in any classical way, and which has in it the heart of quantum mechanics. In reality, it contains the only mystery.” - Richard Feynman http://www.blacklightpower.com/theory/DoubleSlit/ 2 slit interference, one photon Faraday effect The Faraday effect Faraday effect Right and left circularly polarized light have different indexes of refractions http://www.ifm.liu.se/~ulfek/viz/ Faraday effect Verde constant depends on wavelength Jain, Am. J. Phys. 67, August 1999, 714 Zeeman effect The Zeeman effect Zeeman effect The Zeeman effect: Mercury energy levels Zeeman effect Fabry-Perot distinguishes wavelengths Optical Pumping Optical pumping F=2 5P1/2 F=1 795 nm light F=2 5S1/2 462 MHz F=1 Hyperfine mF 2 1 0 -1 -2 B increases Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR B-field Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Organic salt, DPPH Microwaves Microwaves www.microwaves101.com Compton scattering: light as a particle Muon Lifetime Muons are produced in cosmic rays www.lanl.gov Muon Lifetime Properties of the Leptons Particle Symbol Antiparticle Rest mass MeV/c2 L(e) L(muon) L(tau) Lifetime (seconds) Electron e- e+ 0.511 +1 0 0 Stable Neutrino (Electron) νe νe 0(<7 x 10-6) +1 0 0 Stable Muon μ- μ+ 105.7 0 +1 0 2.20x10-6 Neutrino (Muon) νμ νμ 0(<0.27) 0 +1 0 Stable Tau τ- τ+ 1777 0 0 +1 2.96x10-13 Neutrino (Tau) ντ ντ 0(<31) 0 0 +1 Stable www.hyperphysics.phy Muon Lifetime Decay of muon proceeds through the weak interaction Muon Lifetime Muons stopped by plastic scintillator plastic scintillator photo-multiplier tube http://alpha.sci.osaka-cu.ac.jp/grapes3 Muon Lifetime Typical muon-electron pulses from the photomultiplier tube www.prestoncoll.ac.uk Plasma Plasma: “the 4th state of matter” Most common state for the visible matter in the universe. hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu Plasma Langmuir probe used to measure electron temperature Langmuir probe on Cassini/Huygens (Photo: IRF Uppsala) Cassini approaches Saturn (Artist's impression: NASA) Cavendish experiment: measure of G, gravitational constant http://fas.harvard.edu 2 equilibrium positions double the accuracy Experiment 1 order 12:30 Douglass, Scott 12:45 Marcu, Diana M. 1:00 Kolansky, Jeremy 1:15 Moberley, Andrew K. 1:30 Toulouse, Michael W. 1:45 Guthrie, Daniel F. 2:15 Mills, Ashleigh M. 2:30 Crump, Nicholas A. 2:45 Price, Dennis M. 3:00 Cao, Vincent M. 3:15 LePire, Steven D. 3:30 Simingalam, Sina Hall effect Band-gap theory of Solids Mercury