* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint
Arbuscular mycorrhiza wikipedia , lookup
Entomopathogenic nematode wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
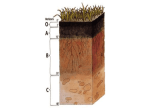
By: Patrick Oney, Melissa Moody, Lacey Dickens, and Jordan Hall •Soil is an earthly material made up of organic material (once living or still living things) and inorganic material (never living things) such as rocks. Soil •Soil is formed by organic material, such as worms or dead animals. It is also formed by inorganic material, such as rocks. The weathering breaks down the rocks over time and the minerals sink into the ground. Then the microbes eat the bacteria and unliving things. After that, the earth worms mix the soil, feed on the leaves, and leave behind castings to fertilize the soil. • If you want to become a soil scientist you need to know about soil. • If you want to plant a garden you need to know what type of plants grow in your soil. A soil profile is a vertical section that reveals all of the soil’s horizons, or layers. Each layer of the soil profile is formed by: • Additions- Materials such as leaves, dust, and chemicals may be added to the soil • Losses- Materials may be lost from the soil as a result of erosion or deep leaching • Translocations- Materials may be moved in the soil due to upward movement by evaporating water • Transformations- Materials may be changed in the soil by organic matter decay, chemical reactions, and weathering of minerals The topsoil layer, the layer right below the ground level, has the most organic material. A soil scientist is a person who studies soil and is qualified to do this. The task they perform is to evaluate and interpret soils and soil-related information. Credits: Microsoft PowerPoint 2003 Clip Art www.wikipedia.org/wiki/Soil www.cnr.berkeley.edu www.ask.com Holt Science and Technology Earth Science textbook