* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8: Geologic Time
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
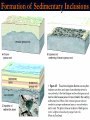
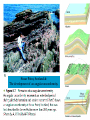
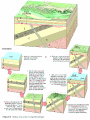
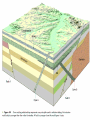
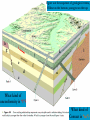
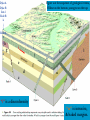
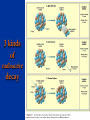
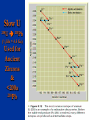
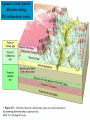
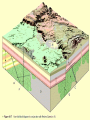
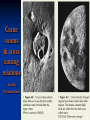
Chapter 8: Geologic Time PowerPoint Presentation Stan Hatfield . SW Illinois College Ken Pinzke . SW Illinois College Charles Henderson . University of Calgary Tark Hamilton . Camosun College Copyright (c) 2005 Pearson Education Canada, Inc. 1 Geological Time is of Vast Duration Sediments were buried under a Mountain Range, metamorphosed, half the crust was uplifted & eroded, glaciers carried it, lake storms removed all but the biggest rocks. Geologic Time Relative age dates – placing rocks and events in their proper sequence of formation. e.g. Tertiary is younger than Cretaceous (rocks, fossils, climate) Numerical dates – specifying the actual number of years that have passed since an event occurred (known as absolute age dating using isotope clocks) Geologic time scale – Earth’s history is ~4.5 Ga long and written disproportionately by the rocks formed and processes which operated at different times and places. Ordovician Strata: Chute Vernal, PQ Relative Dating – Key Principles Law of Superposition Developed by the Danish physician Nicolaus Steno working in Italy in 1669 In an undeformed sequence of sedimentary rocks (or layered igneous rocks), the oldest rocks are on the bottom Most sedimentary & volcanic rocks are deposited in sequences of essentially flat lying beds Relative Dating – Key Principles Principle of Original Horizontality Layers of sediment are generally deposited in a horizontal position Rock layers that are flat have not been disturbed Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships Younger features cut across older features Principle of Inclusions Younger rocks/features include older ones All 3 types of rocks can include older rocks and minerals Relative Dating – Key Principles: Horizontality & Law of Superposition Correlation Permian Strata, South Rim Lower Paleozoic Strata: Devon, UK Fold Hinge Deposition, Deformation At the Closing of Iapetus Formation of Sedimentary Inclusions Relative Dating – Key Principles Unconformities Types of Unconformities Disconformity – strata on either side of the unconformity are parallel (least missing time) Angular unconformity – tilted rocks are overlain by flat-lying rocks (10’s of Ma missing) Nonconformity – metamorphic or igneous rocks in contact with sedimentary strata (most missing time, eroded down to crystalline basement rocks) Siccar Point, Scotland & The development of an angular unconformity. Figure out the sequence of geological events, Oldest on the bottom, youngest on the top. m h g i j e c k l f d What kind of unconformity is “i”? What kind of Contact is “m”? Dyke A Dyke B Intr-l Fault B k j I Fault A h g fh e g d c Figure out the sequence of geological events, Oldest on the bottom, youngest on the top. m i j e c k l f d “i” is a disconformity “m” is intrusive, & baked margins. Which type of unconformity here at the South Rim represents the greatest amount of missing time and why? Correlation of Rock Layers Matching of rocks of similar ages in different regions is known as correlation Correlation often relies upon fossils William Smith (late 1700s and early 1800s) noted that sedimentary strata in widely separated areas could be identified and correlated by their distinctive fossil content Other than fossils we often rely on widespread instantaneous events like volcanic ash falls Unconformities bound packages of stratigraphy Correlation across slightly overlapping stratigraphy Arizona to Utah. Correlation of Rock Layers Correlation Principle often relies upon fossils of Fossil (Faunal) Succession – fossil organisms succeed one another in a definite and determinable order that documents the evolution of life; therefore any time period can be recognized by its fossil content Index fossils – represent best fossils for correlation; they are widespread ecologically & geographically and are limited to a short time span (i.e., they evolved rapidly) Time from Concurrent Range Zones Dating with Radioactivity Reviewing Isotope Basic Atomic Structure (only a few of these are radioactive) Variant of the same parent atom, same atomic number Differs in the number of neutrons (weight) Results in a different mass number than the common type of atom for this element Too many additional neutrons makes a nucleus unstable and prone to radioactive decay 3 kinds of radioactive decay Dating with Radioactivity Parent – an unstable radioactive isotope Daughter product – the isotopes that result from the decay of a parent Half-Life – the time required for one-half of the radioactive nuclei in a sample to decay Half-life differs for every Parent-Daughter pair of isotopes Exponential Decay of Parent Isotopes (& exponential growth of daughters) The Decay Equation: A = A0 e –λt A0 is the initial amount of the parent isotope Dating with Radioactivity Radiometric Principle The Dating of Radioactive Dating percentage of radioactive atoms that decay during one half-life is always the same (50 percent) However, the actual number of atoms that decay continually decreases Comparing the ratio of parent to daughter yields the age of the sample Dating with Radioactivity Radiometric dating Useful radioactive isotopes for providing radiometric ages Rubidium-87 Strontium-87 ~Precambrian Feldspar, micas, amphiboles Thorium-232 Lead-207 ~Pc Zircon Two isotopes of uranium (235 and 238) to Lead (208 & 206), 4.5 Ga & 713 Ma respectively, ~Pc to Mesozoic Zircon Potassium-40 Argon-40 or relative to Argon-39 >2 Ma Feldspar, micas, volcanic glass Slow U 238U 210Pb (½ life = 4.5 Ga) Used for Ancient Zircons & <200a 210Pb Dating with Radioactivity Rules for Radiometric Dating Mineral contains both parent & daughter as for Zircon with 238U and 206Pb or feldspar with 87Rb and 87Sr Formed at time of event to be dated as for a lava flow, dyke or contact metamorphism The mineral is a closed system and has neither gained nor lost parent & daughter Dating with Radioactivity Radiometric Sources A dating of error closed system is required If temperature is too high, daughter products may be lost To avoid potential problems, only fresh, unweathered rock samples should be used Production of 14C in the upper atmosphere (& decay once organisms die) Cosmic rays Expel neutrons from Atmospheric gases (N,O). This expels a proton From nitrogen Forming radioactive 14C. The extra neutron in radioactive 14C decays back to 14N With a ½ life of 5730 years. Dating with Radioactivity Dating dating) with carbon-14 (radiocarbon Half-life of only 5730 years Used to date very recent events Carbon-14 is produced in the upper atmosphere Useful tool for anthropologists, archaeologists, historians, and geologists who study very recent Earth history Only works for plant or animal tissue, not rocks The Geological Time Scale Geologic Time Scale Structure Names of the geologic time scale of the eons Phanerozoic (“visible life”) – the most recent eon, began just over 540 million years ago Proterozoic Archean Hadean – the oldest eon The Geological Time Scale Geologic Time Scale Structure Era of the geologic time scale – subdivision of an eon Eras of the Phanerozoic eon Cenozoic (“recent life”) Mesozoic (“middle life”) Paleozoic (“ancient life”) Eras are subdivided into periods Periods are subdivided into Epochs Precambrian time Nearly 4 billion years prior to the Cambrian period Not divided into smaller time units because the events of Precambrian history are not known in great enough detail Also, first abundant fossil evidence does not appear until the beginning of the Cambrian Difficulties time scale in dating the geologic Not all rocks can be dated by radiometric methods Grains comprising detrital sedimentary rocks are older than the rock in which they formed The age of a particular mineral in a metamorphic rock may not necessarily represent the time when the rock formed as porphyroblasts may grow for many Ma The rock needs minerals with the right parent and daughter isotope pairs and in the right age span to be measureable. Difficulties in dating the geologic time scale Datable materials (such as volcanic ash beds and igneous intrusions) are often used to bracket various episodes in Earth history and arrive at ages Dates change as brackets become narrower and methods refined; e.g., base of Triassic is now 252 Ma, base of Permian is now 299 Ma, base of Cambrian is 543 Ma… Igneous events permit Absolute dating Of sedimentary rocks. Dating Terrains On other Worlds Crater counts & cross cutting relations mostly Precambrian Dendrochronology (wiggle matching) For wood in 14C realm <70Ka Extinctions: Dinosaur Graveyards Bolide impact & Deccan Trap Volcanism both occur at 65Ma. Biodiversity dwindled for 10 Ma prior to this. The K/T massive extinction is debated.