* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nuclear powperpoint
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Technetium-99m wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
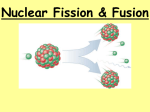
Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear • Radioactivity – the process by which materials give off rays and particles. • Radiation – penetrating rays and particles emitted by a radioactive substance. • Radioisotopes – unstable nuclei Nuclear Radioactive substances emit radiant energy because they are unstable They are unstable because of the protonneutron ratio. *Neutrons act as “insulation” or “glue” to help keep the nucleus from breaking apart *When there are too few neutrons, or too many neutrons, the nucleus will want to give off energy Reactions Chemical reactions vs. Nuclear Reactions *Chemical reaction- atoms gain or lose electrons, change their electron configuration *Nuclear reaction- atoms gain or lose protons, neutrons, or energy; cannot be sped up, slowed down or stopped. Dalton was wrong- atoms are divisible An unstable nucleus releases energy by emitting radiation during radioactive decay. Definitions • Parent nuclei- nucleus that breaks apart. • Daughter nuclei- nucleus that is formed. *The total mass and charge should be conserved in a nuclear reaction (law of conservation of mass) Types of decay cont. Alpha Radiation (α) *emit a particle that has 2 protons, 2 neutrons *resembles a Helium atom 238 * 4 He + 234 Th U 92 2 90 the sum of the mass numbers (superscripts) on the right MUST equal the sum on the left * the sum of the atomic numbers (subscripts) on the right MUST equal the sum on the left Types of Rxns cont. Beta radiation (β) *emit an electron *How? A neutron breaks apart into a proton and electron. *The electron is ejected, the proton stays inside 1 neutron 1 proton + 0 electron 0 1 -1 *the nucleus loses a neutron and electron, but gains a proton 14 C 14 N + 0 e 6 7 -1 *the sum of mass and atomic numbers MUST be equal on the left and right Types of Rxns cont. Gamma radiation (γ) *Release high-energy photon (called a gamma ray) 230 Th 230 Th + 0 γ 90 90 0 *Emitting a gamma ray does not change the mass or atomic numbers Radiation Graph Particle Symbol Notation Penetration Damage alpha α 4 He 2 least most beta β 0 e -1 medium medium gamma γ 0 0γ most least Bombardment rxns A high energy particle is fired at an unstable isotope, resulting in a nuclear reaction Can bombard with alpha particles, neutrons, or protons Use this type of reaction to create artificial elements (Plutonium, Neptunium, etc.) 238 U 92 + 10n 23993 Np + 0-1e fission *The splitting of a nucleus into smaller fragments When nuclei of certain isotopes are bombarded with a neutron, they undergo fission Uranium-235 and Plutonium-239 are the only nuclei that can undergo fission 235 U + 1 n 91 Kr + 142 Ba +1 n 92 0 36 56 0 Fission cont. Chain Reaction: some of the neutrons released react with other fissionable atoms, producing more neutrons which produces more fission reaction Atom Bombs Devices that start uncontrolled nuclear chain reactions When the US dropped them in Japan-120,000 people died instantly Need enough uranium or plutonium to reach supercritical mass Once you have supercritical mass, you can start the chain reaction Atom Bombs cont. Manhattan project-name of the project that developed the A-bomb *Dr. Oppenheimer led the project Who has tested A-bombs? USA, Soviet Union, United Kingdom, France, China, India, Pakistan and North Korea Nuclear Reactors *use controlled fission reactions to produce energy Nuclear Reactors cont. Nuclear Waste *Fuel rods from nuclear power plants are one source of nuclear waste. *Fuel rods contain some Uranium-235 or Plutonium-239 *takes a long time (more than a decade) for any remaining radioactive fuel to decay *the fuel rods must be stored in water cooling tanks or stored off-site Fusion *when nuclei combine to produce a nucleus of greater mass. The energy released by the sun is a result of fusion *Hydrogen nuclei fuse to make Helium nuclei Releases much more energy that fission reactions They can only occur at extremely high temperatures (excess of 40,000,000°C)and are difficult to control Fusion cont. Scientists are interested in fusion because the fuel is cheap and available. 2 H 1 + 31H 42He + 10n + energy Hydrogen Bomb Based on fusion reactions 10 times more powerful than the atomic bomb USA, Russia, United Kingdom, France and China have tested H-bombs Contains an atomic core: once fission occurs, the temperature becomes high enough to allow for the fusion rxn. Fusion rxn produces a shock wave (extremely high pressure gas) that causes damage Radiation Uses Radiation cannot be seen, heard, felt, or smelled Radiation detector machines to detect radiation (Geiger counter, Scintillation counter, film badge) Radiation can be harmful because it causes damage to body tissue It can also be used to trace, diagnose diseases and treat cancer