* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint - Valence Electrons
Group 12 element wikipedia , lookup
Boron group wikipedia , lookup
Dmitri Mendeleev wikipedia , lookup
Alkali metal wikipedia , lookup
Group 3 element wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Period 6 element wikipedia , lookup
Period 3 element wikipedia , lookup
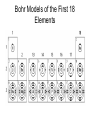
Chapter 2 – Elements and The Periodic Table Elements • Element – a type of matter made up of only one kind of atom (e.g. periodic table). • Atom – smallest particle of an element that still retains all the properties of that element. • Compound – 2 or more elements joined (e.g. H2O). • Molecule – 2 or more atoms combined (e.g. CO carbon monoxide; O2 oxygen gas). Symbols Off the Periodic Table • • • • The symbols on the Periodic Table are universal (used world-wide) Symbols come from Latin (or Greek) words CAPITALIZE the first letter Lower case 2nd letter (if it is needed) e.g. No vs. NO Who created the Periodic Table? Section 2.2 • Born : 1834 Died : 1907 Nationality : Russian Occupation : Chemist • Dmitri Mendeleev brought order to the chaos of chemistry by asserting his periodic law, which states that the elements arrange themselves according to their atomic number and their chemical properties. How is the Periodic Table set up? • Elements are listed horizontally according to their atomic number (number of protons). • Periods are the horizontal rows of elements. • Elements are listed vertically according to their chemical properties. • Groups or Families are arranged vertically. Alkaline Earth Alkali Metals Metals Groups Halogens Noble Gases Atomic Number and Atomic Mass • Atomic number = number of protons found in the nucleus. – Ex. Oxygen’s atomic number is 8 • Atomic mass = mass of an average atom of an element. Measured in atomic mass units (amu) Atomic number Symbol Atomic mass Alkali Metals • Highly reactive – Reactivity increases as you go down the group. • • • • • Metals React with both oxygen and water. Soft Low melting points Have a +1 ion charge Alkaline Earth Metals • • • • Less reactive than alkali metals Metals Burn in air if heated Produce bright flames and used in fireworks. • Will react with water, but not as vigorously as alkali metals • Have a +2 ion charge Halogens • • • • • • Non-metals Highly reactive F and Cl are gases at room temperature Br is a liquid and I is a solid F is the most reactive and I is the least Have a -1 ion charge Noble Gases • • • • • • Most stable and unreactive elements They are colourless, odourless gases Ar and Ne are used in light fixtures Non-metals “Royal” Have a 0 ion charge Metals, Non-metals, and Metalloids Table 2.2 - Properties State at Room Temperature Appearance Conductivity Malleability and Ductility Metals - Solid except Mercury - shiny luster - good conductors of heat and electricity - malleable - ductile Non-metals - some gases or solids -bromine is a liquid - not very shiny - poor conductors of heat and electricity - brittle - not ductile Metalloids - solids - can be shiny or dull - may conduct electricity - poor conductors of heat - brittle - not ductile Section 2.3 - Electron Shells: 3-D Outside the Nucleus • The way an element chemically reacts depends on the number of electrons in it’s outer shell. • Atoms are stable when their outer shells are full of electrons. • If a shell is not full, the atom is reactive, and it either wants to fill its outer orbital or get rid of it altogether. Shell (orbital) Maximum # of e- 1 2 2 8 3 8 4 18 Just use this table for our purposes in grade 9 Bohr Model Diagrams • It has 8 e- in outer shell. • Doesn’t react! • Noble Gas Look at the outer shell. Examples when outer shell is not full Look at the outer shell of each: – Outer shells not full. – Reactive! Lithium Lithium will donate 1 eand Fluorine borrow 1 eFluorine Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are found in the outermost shell. • Most elements in the same family have the same number of valence electrons Examples: Halogens = seven valence electrons Alkali = one valence electron Alkali Earth metals = two valence electrons Noble Gases - are stable and non-reactive because they are full in the outer most valence shell. Bohr Models of the First 18 Elements Ion Charge or Combining Capacity • The ion charge is an electric charge that forms on an atom when it gains or loses electrons. • Any electrically charged atom is called an ion. • If an atom has gained electrons, it will be negatively charged. – Usually non-metals • If an atom has lost electrons, it will be positively charged. – Usually metals