* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nuc_alchemy_talk-fgs-dec07
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
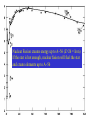
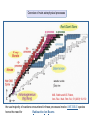
Making Gold : Nuclear Alchemy Dr. Paddy Regan Department of Physics University of Surrey Guildford, GU2 7XH [email protected] Medieval alchemist…trying to turn base metals into gold… Mistake…to try and use ‘chemistry’…needed nuclear physics!! ‘Elemental my dear…..’ Mendeleyev Moseley’s Law….evidence for Atomic numbers…. ‘Characteristic’ X-rays…with a chemical (Z) dependence X-rays come from atomic ‘vacancies’ i.e. holes in the electron shells around the atom. Quantum mechanics means that the electron orbits are fixed in energy…. X-rays come from an electron ‘dropping’ from one energy level to a lower one X-rays come from atomic ‘vacancies’ i.e. holes in the electron shells around the atom. Quantum mechanics means that the electron orbits are fixed in energy…. X-rays come from an electron ‘dropping’ from one energy level to a lower one X-rays come from atomic ‘vacancies’ i.e. holes in the electron shells around the atom. Quantum mechanics means that the electron orbits are fixed in energy…. X-rays come from an electron ‘dropping’ from one energy level to a lower one X-ray emitted Inside a nucleus 2 protons + 2 neutrons = 4He Neutron, changes mass, No charge. ~10-15m 3 protons + 4 neutrons = 7Li Proton, changes mass and charge, atomic number (Z) = number of protons in atomic nucleus How it all starts….Hydrogen (Z=1) to Helium (Z=2) proton-proton chain proton-proton chain p + p d + e+ + n p + d 3He + g 86% 3He 14% + 3He 4He + 2p 3He 99.7% PP-I Qeff= 26.20 MeV + 4He 7Be + g + e- 7Li + n 7Li + p 2 4He 7Be 0.3% + p 8B + g 8B 8Be + e+ + n 7Be PP-II 2 4He Qeff= 25.66 MeV PP-III Qeff= 19.17 MeV net result: 4p 4He + 2e+ + 2n + Qeff Spectral Maps of the Galaxy Ref http://adc.gsfc.nasa.gov/mw/mmw_images.html Nuclear Fusion creates energy up to A~56 (Z=26 = Iron) If the star is hot enough, nuclear fusion will fuel the star and create elements up to A~56 SN1987a before and after !! Figure Wiescher, Regan & Aprahamian, Physics World Feb. 2002, page 33-38 Slow-neutron capture process allows formation of elements from A~56 to A=209 (Bi)... terminates at 209Bi...why? Neutron capture… no electrostatic barrier to nuclear fusion…. all you need are enough Neutrons… Beta –radioactive decay, (consequence of E=mc2) 2 types: (i) Beta- plus proton changes to a neutron (Z ->Z-1) (ii) Beta – minus neutron changes to a proton (Z -> Z+1) Nuclear reactions in Red giant stars create ‘spare’ neutrons So, how do you make Gold ? • Gold has 79 protons (i.e. Z=79) • Start with Z=78 protons (i.e. Platinum) • Specifically 196Pt ( Pt = Z=78, N=196-78=118) • Reaction is 196Pt + neutron to make 197Pt • 197Pt is radioactive and ‘beta-decays’ to make 197Au (i.e., normal ‘stable’ gold’ The Natural Decay Chain for 238U Qa(210Pb) = 5.41 MeV Ea = 5.30 MeV E(206Pb) = 0.11 MeV T1/2 = 138 days. ‘Radium’ ‘218At =Radium B’ 210Po Radon =‘Emanation’ =Radium ‘F’ C’ E D C C’’ ‘218Po =Radium A’ S-process makes 209Bi from 208Pb+n → 209Pb (T1/2=3.2hr) → 209Bi Neutron capture on stable 210Po 209Bi → 210Bi (T1/2 =5 days) → 210Po. → a + 206Pb (stable nucleus, as is 207Pb and 208Pb). Overview of main astrophysical processes M.S. Smith and K.E. Rehm, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci, 51 (2001) 91-130 the vast majority of reactions encountered in these processes involve UNSTABLE species hence the need for Radioactive Ion Beams Summary What’s made where and how ? – Hydrogen to Helium (in the sun, p-p chain CNO cycles). – Helium to Carbon (a story for another day) – Carbon to iron: nuclear fusion reactions – Iron to Uranium • Up to 209Bi (210Po end-point) slow neutron capture • Heavier than Bismuth (Z=83), rapid neutron capture, supernovae.