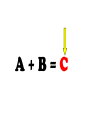* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File Vocabulary PPT set #1
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Stokes wave wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
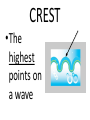
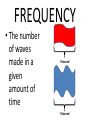
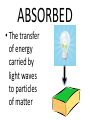
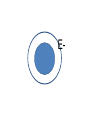
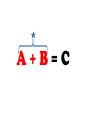
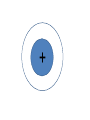
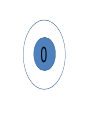
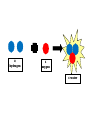
FORCE • Push or a pull – measured in Newton’s (N) BALANCED FORCES • Equal forces acting on an object in opposite directions UNBALANCED FORCES • Causes a change in the speed or direction of an object’s motion GRAVITY • The force of attraction between two objects INERTIA • The tendency of all objects to resist any change in motion – Things want to keep doing what they are doing WAVES • A back and forth motion that carries energy through matter or through space CREST •The highest points on a wave TROUGH •The lowest points on a wave MEDIUM / MEDIA • A substance (solids, liquids, gases) through which a wave can travel WAVELENGTH • The distance from one point on a wave to the next corresponding point – from one crest to another AMPLITUDE • A measure of the wave’s height from the resting position. Larger amplitudes carry more energy. FREQUENCY • The number of waves made in a given amount of time 1 Second 1 Second ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES • A wave that can travel through space and matter and consists of vibrating electric and magnetic fields MECHANICAL WAVES • A wave that travels only through matter by creating vibrations in a medium VISIBLE LIGHT • The very narrow range of wavelengths and frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum that humans can see REFLECTED • The bouncing back of a wave after the wave hits a barrier REFRACTED • The bending of a wave as the wave passes at an angle ABSORBED • The transfer of energy carried by light waves to particles of matter TRANSMITTED •The passing of light through matter PHYSICAL PROPERTIES • Properties that DO NOT change the chemical nature of matter – color, texture, odor, density, malleable, ductile… CHEMICAL PROPERTIES • Properties that DO change the chemical nature of matter – flammability and reactivity ATOMS • The smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance NUCLEUS • The tiny, very dense, positively charged region in the center of an atom; made of protons and neutrons PROTONS • A positively charged subatomic particle of the nucleus of an atom – same as the atomic number + ELECTRONS • Negatively charged subatomic particle that is found in all atoms - NEUTRONS • A subatomic particle of the nucleus of an atom that has no charge 0 ELECTRON CLOUD • A region inside an atom where electrons are likely to be found ATOMIC NUMBER • The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom #5 ELEMENTS • A pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means PERIODIC TABLE • An arrangement of the elements according to their atomic numbers CHEMICAL SYMBOL • An abbreviation of a chemical element using one or two letters – ex: H = hydrogen •Sodium = •Na FAMILIES / GROUPS • Elements that are grouped together based on their chemical properties and reactivity REACTANTS • A starting material in a chemical reaction. A+B=C PRODUCTS • A substance formed from a chemical reaction A+B=C COMPOUNDS • A pure substance composed of two or more elements that are chemically combined 2 hydrogen 1 oxygen 1 water TEST YOURSELF! Push or a pull – measured in Newton’s (N) •Sodium = •Na 1 Second 1 Second The bending of a wave as the wave passes at an angle E- A+B=C Equal forces acting on an object in opposite directions A pure substance composed of two or more elements that are chemically combined A wave that can travel through space and matter and consists of vibrating electric and magnetic fields A+B=C A subatomic particle of the nucleus of an atom that has no charge Properties that DO NOT change the chemical nature of matter – color, texture, odor, density, malleable, ductile… + Elements that are grouped together based on their chemical properties and reactivity The highest points on a wave 0 2 hydrogen 1 oxygen 1 water #5