* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbon Capture and Storage The Developments Worldwide
Energiewende in Germany wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Climate Change conference wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Carbon capture and storage wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
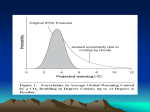
Carbon Capture and Storage The Developments Worldwide Tim Dixon IEA Greenhouse Gas R&D Programme EEF - February 19th 2008 www.ieagreen.org.uk Introduction • Introduction to IEA GHG • What at iss CCS ? • Why CCS ? Fossil fuels and climate change • Is it safe ? • International policy and regulatory developments • International project developments www.ieagreen.org.uk IEA Greenhouse Gas R&D Programme • • A collaborative research programme founded in 1991 Aim is to: Provide members with definitive information on the role that technology can play in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. • Producing information that is: • Objective, trustworthy, independent • Policy relevant but NOT policy prescriptive • Reviewed by y external Expert p Reviewers • Subject to review of policy implications by Members • Activities: Studies (>100), R&D networks (6), Communications :f ilit ti and facilitating d focussing f i R&D and d demonstration d t ti activities ti iti Funding approximately 2 million €/year. • www.ieagreen.org.uk www.ieagreen.org.uk What is Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)? www.ieagreen.org.uk Carbon Capture and Storage Capture 85-90% Transport Storage www.ieagreen.org.uk CO2 Storage • Saline Aquifers • Depleted oil/gas reservoirs • Enhanced Oil Recovery • Enhanced Coal Bed Methane www.ieagreen.org.uk CO2 Trapping Mechanisms • Physically trapped beneath caprock timescale: immediately • CO2 is trapped by capillary forces timescale: 1- 100s yrs • CO2 dissolves in water timescale: 1-1000s yrs • CO2 converts to solid minerals timescale: 100s – 10,000s yrs • Trapping becomes more secure with time www.ieagreen.org.uk CO2 Storage Capacity Storage Option Global C Capacity it - Gt CO2 Depleted gas fields 690 Depleted oil fields/CO2EOR 120 Deep saline aquifers 400 - 10 000 Unminable coal seams 40 Global CO2 emissions ~30 Gt pa www.ieagreen.org.uk Costs - UK power generation costs ((central assumptions with EU EU--ETS)) Offshore Wind (100MW) Onshore Wind (80MW) Nuclear CCGT with CCS IGCC with CCS •ROC buyout price •Market Market price price 2006 PF with FGD with CCS Retrofit PF with FGD with CCS CCGT Market price 02/2008 IGCC PF with FGD 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 £/MWh Ie CCS = 12.5-25% increase coe www.ieagreen.org.uk •UK DTI Energy Review 2006 Why CCS ? www.ieagreen.org.uk Predicted Future Global Warming •Global Temperature •Global CO2 Emissions •Source: IPCC 2007 www.ieagreen.org.uk 12 STERN REVIEW: The Economics of Climate Change (already at about 430 ppm CO2e – all GHG GHG, not just CO2) www.ieagreen.org.uk World Primary Energy Demand •Other renewables •Biomass •Hydro •Nuclear •Gas •Oil Oil •Coal •billionn tonnes of ooil equivalent •18 •16 •14 •12 •10 •8 •66 •4 •2 •0 •1980 •1990 •2000 •2010 •2020 •2030 Global demand grows by more than half over the next quarter of a century, with coal use rising most in absolute terms (IEA/OEACD WEO 2007) www.ieagreen.org.uk Reference Scenario: China & India in Global CO2 Emissions •Cumulative Energy-Related CO2 Emissions •United States •European Union •Japan •China •1900-2005 •2006-2030 •India •0 •100 •200 •300 •billion tonnes •400 •500 •Around 60% of the global increase in emissions in 2005 2005-2030 2030 •comes from China & India www.ieagreen.org.uk No one solution is enough 45 42 Gt CCS in industry - 3% CCS in power generation - 9% Nuclear - 13% 40 Renewables - 20% 35 2 30 End Use electricity efficiency - 17% Gt of CO Switching from coal to gas - 8% 25 E d Use End U fuel f l efficiency ffi i - 30% 27 Gt 20 23 Gt Source: IEA World Energy Outlook 2007 15 10 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 2030 •WEO Conclusion : Next 10 years are critical - The pace of capacity additions will be most rapid - Technologywww.ieagreen.org.uk will be “locked-in” for decades Role of CCS in climate change mitigation? • IPCC Special Report (2005) – CCS contributing 15-55% of CO2 mitigation to 2100 gy Perspectives p ((2006)) – CCS 20-28% of • IEA Technology mitigation to 2050. Second only to energy efficiency. • Stern Report (2006) – CCS ~10% mitigation by 2025, ~20% by 2050 Marginal 2050. M i l mitigation iti ti costs t without ith t CCS iincrease b by ~60%. 60% • EC/Shell (2007) - 7 yrs delay CCS = 90GT CO2 to 2050 = 3 yrs global emissions = 10ppm • World Energy Outlook 2007. “CCS is one of the most promising routes for mitigating emissions in the longer term and could reconcile continued coal burning with the need to cut emissions in the longer term”. www.ieagreen.org.uk Is it Safe ? www.ieagreen.org.uk IPCC Special Report on CCS (2005) • “Observations from engineered and natural analogues as well as models suggest that the fraction retained in appropriately selected and managed geological reservoirs is very likely to exceed 99% over 100 years and is likely to exceed 99% over 1,000 years. “ • “For well-selected, designed and managed sites, the vast majority of the CO2 will gradually be immobilized by various trapping mechanisms and, in that case case, could be retained for up to millions of years. years Storage could become more secure over longer timescales. ” • “Local health and safety risks for CO2 pipelines could be similar or lower than hydrocarbon pipelines.” www.ieagreen.org.uk IPCC Guidelines for GHG Inventories • • Apr 2006 Vol 2 Energy, Chp 5 - CO2 Transport, Injection and Geological Storage • Methodology Site characterisation – inc leakage pathways Assessment of risk of leakage – simulation / modelling Monitoring g – monitoring gp plan Reporting – inc CO2 inj and emissions from storage site • For appropriately selected and managed sites, supports zero leakage assumption unless monitoring indicates otherwise www.ieagreen.org.uk IPCC Guidelines for GHG – cont. Monitoring Plan • • • • • Measurement of background fluxes of CO2 Continuous measurement of CO2 injected Monitoring of injection emissions P i di monitoring Periodic it i off CO2 di distribution t ib ti Monitoring of CO2 fluxes to surface • Post-injection j monitoring g – as above,, linked to modelling, g, may y be reduced or discontinued once CO2 stabilises at its predicted longterm distribution Incorporate improvements in technologies and techniques over time • Monitoring technologies – Annex 1 • Deep subsurface technologies • Shallow subsurface technologies • Surface / water technologies www.ieagreen.org.uk Site Characterisation and Modelling Year 2021 Y Year 5019 Year 2412 Year 2621 Year 7018 •Kilde: Gemini No. 1, 2004 (NTNU and Sintef) www.ieagreen.org.uk Monitoring 4D seismic used to monitor the CO2 plume Statoil 2007 www.ieagreen.org.uk If leakage were to occur ? Remediation methods available from oil and g gas expertise p • Well integrity • • • • Re-seal and re-plug well (cement, heavy mud) Repair or replace well casing/tubing/packing Intercept well - long-established techniques • Caprock C k • • • • Remove accumulated CO2 Reduce pressure in reservoir Increase pressure in strata above Inject sealing foam/gel/cement • Costs - ~ 1-10 $ $m • Also can stop using site www.ieagreen.org.uk I t International ti l Policy P li and dR Regulatory l t Developments www.ieagreen.org.uk London Convention and Protocol • • Marine Treaty - Global agreement regulating disposal of wastes and other matter at sea Convention 1972 ((83 countries), ), Protocol 1996 – ratified March 2006 (31 countries) CCS • CCS scenarios prohibited by LP - considered as disposal • Assessed by LC Scientific Group • 2006 - Risk Assessment Framework for CO2 • Amendment adopted at 28th Consultative Meeting, 2 Nov 2006 p of:came into force 10 Feb 2007 - to allow disposal “ CO2 streams from CO2 capture processes for sequestration...” www.ieagreen.org.uk Simulated and observed marine pH g till 2100 ranges 8.6 8.4 •pH range for the last 20 million years 8.2 pH 8 7.8 7.6 7.4 7.2 7 190 ppm 280 ppm 370 ppm 500 ppm Glacial Pre-ind Now 2050 700 ppm 1000 ppm www.ieagreen.org.uk 2100 2100 worst case PML 2005 •PML: Impacts and Feedbacks in a High CO2 World? •Synergistic Effects •Climate Change •Ocean Acidification •Feedbacks with ocean acidification •Increased thermal and freshwater stratification •Biogases: sea/air flux •Feedbacks with climate change •CH4, N2O, DMS… •Decreasing surface ocean pH •Ocean CO2 uptake •C, N, •P, Si, S Modelling •Pelagic biodiversity and biogeochemistry Experimentation •Decreasing nutrient and O2 flux Observation •Benthic-Pelagic coupling •Benthic biodiversity and biogeochemistry •Turley, Plymouth Marine Laboratory www.ieagreen.org.uk •Meroplankton: larvae and juveniles Example: Leakage at a rate of 3 million tons CO2 per year •Slide courtesy Ken Caldeira; Data Chen et al., 2005 www.ieagreen.org.uk Simulation of a continuous leak over 1 year pH anomaly compared with no leak - based on capacity of one pipeline •-0.02 Short term leak will have a very small and spatially limited impact A long term leak will have a measurable and wider spread impact, but the impact is small compared with atmospherically driven acidification Blackford, J.C., Gilbert, F.J., 2007. pH variability and CO2 induced acidification in the North Sea. Journal of Marine Systems 64 www.ieagreen.org.uk OSPAR • • Marine Treaty y for NE Atlantic 15 nations and EC • • • CCS scenarios prohibited Considered CO2 impacts on seas Considered CCS • OSPAR amendments (to Annexes II and III) for CO2 storage adopted June 2007 • OS OSPAR Decision – requirement to use Guidelines G when permitting, including risk assessment and management process • OSPAR Guidelines for Risk Assessment and Management of Storage of CO2 in Geological Formations www.ieagreen.org.uk EC Draft CCS Directive Enabling regulatory framework to ensure environmentally sound CCS (23 Jan 2008) • • • • • • • • • • Follows IPCC GHG Guidelines and OSPAR Objective is permanent storage Permits will be required for CCS Permit only y if “no significant g risk of leakage” g Emphasis on site selection, characterisation, risk assessment, monitoring Corrective measures Financial security required from operator Liability transfer to regulatory authority “when evidence indicates contained for indefinate future” – only then may monitoring reduce or cease Removes regulatory g y barriers in other Directives – IPPC,, Waste,, LCPD,, Water, EIA, ELD Capture-ready www.ieagreen.org.uk ETS Directive To strengthen, expand and improve the ETS from 2013 CCS • Can already be included in Phase II (2008-2012) by ‘opt-in’ • CCS fully included from 2013 • Site and operation will need to comply with CCS Directive • Needs monitoring and reporting guidelines • No free allocation to CCS (same as electricity) • Separate permitting of capture, transport and storage • If any leakage – surrendering of allowances www.ieagreen.org.uk Regulatory developments in other regions • USA – Existing Underground Injection Control programme for ground water protection adapted for Pilot projects • Interstate Oil and Gas Compact Commission has developed recommendations for regulations for CO2 storage at a State Level • US EPA are developing Federal level regulations for CO2 storage • Australia • Will adapt Federal Oil and Gas Laws • State of Victoria has a consultation document for CCS • Canada • Canada – acid gas injection and CO2-EOR already permitted in states like Alberta • Federal Task Force developing CCS regulations • Japan • • Adapted marine laws but has no oil and gas laws to adopt for CCS M t existing Most i ti llaws cover; permitting, itti construction, t ti operational ti l and d abandonment phases but NOT post closure www.ieagreen.org.uk Multinational Initiatives • Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum • To facilitate development and deployment of improved cost-effective technologies for CCS • 2003. 21 Countries and EC • Asia Pacific Partnership on Clean Development and Climate • To accelerate the development and deployment of clean energy technologies • 2006. 6 Countries • G8 – 2005. 5 initiatives on CCS • EU-China EU China Near Zero Emissions Coal project (NZEC) 2005 • Feasibility study for CCS in China, leading towards demonstration www.ieagreen.org.uk International CCS Project Developments www.ieagreen.org.uk Current CO2 Injection and Storage Projects 50 Acid Gas injection sites in North America 4 New CO2-EOR Pilots in Canada Snohvit Sleipner Zama P Penn West W t Weyburn •Mountaineer Alberta ECBM Teapot Dome Rangely Burlington K-12B K 12B CO2 SINK RECOPOL •Qinshui Basin •West Pearl Queen •Frio •Carson Hokkaido Nagaoka In Salah 70 CO2-EOR projects in U.S.A. Key Depleted Oil Field ECBM projects Otway Basin EOR projects j t Gas production Fields Saline aquifier www.ieagreen.org.uk Proposed Integrated CCS Projects SaskPower FutureGen HALTEN DF1 Mongstad Centrica E.ON E.ON RWE RWE HypoGen Lacq GREENGEN DF2 DF4 nZEC Key Stanwell LNG DF3 Pre-Combustion Capture Callide Hazelwood IGCC Oxy-Fuel Post-Combustion www.ieagreen.org.uk Sleipner,, Norway – injecting 1mt since 1997 Sleipner www.ieagreen.org.uk Sleipner www.ieagreen.org.uk In Salah • Algeria • BP with Sonatrach & Statiol • Started in 2004 • Natural gas clean-up • Storing 1 million tons of CO2 annually • Injecting into reservoir aquifer www.ieagreen.org.uk Weyburn • Capture from coal gasification in the USA by Dakota Gas • Injection for enhanced oil recovery in Canada by Encana www.ieagreen.org.uk Recent Project Developments in EU....... Including: g • UK • CCS demo – full scale, coal, post-combustion, offshore storage • Germany • Ketzin - injection • RWE planning a 450 MWe coal fired IGCC project with on-shore storage • Vattenfall have a built a 30 MW CO2 capture pilot plant • Plans to build a 300MW demonstration project in Germany • EON and Siemens – CO2 capture pilot plant • France F • Lacq Project. Total. 2008. Oxyfuel. 150kt - CO2 aquifer. 27km pipeline • Netherlands • CO2 injection into K12B field • NUON _ IGCC CO2 capture www.ieagreen.org.uk IEA Greenhouse Gas R&D Programme • General - www.ieagreen.org.uk g g • CCS - www.co2captureandstorage.info •GHGT-9 •16th – 19th November 2009 •Washington D.C. •www.mit.edu/ghgt9 www.ieagreen.org.uk