* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sealevel - Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
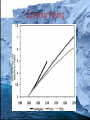
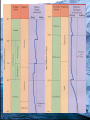
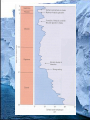
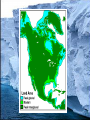
Global Change In Sea Level Seds Lab 9 Currently Rising May lead to • • • • Loss of property and coastal habitats Flood risk and potential loss of life Loss of renewable/subsistence resources Loss of Tourism, Recreation and Transportation Functions • Loss of non-monetary cultural resources • Loss in agriculture/aquaculture History • Evidence from Fossil and Sedimentary Record • Correlation in time in significant part of sedimentary record • Oxygen isotope evidence from plankton or ice cores Mass Extinctions • Strong relationship between Eustatic sea level and Mass Extinctions • 5 of 6 show evident correlation Ordovician Permian Triassic Cretaceous Late Devonian Methods of Sea-Level Change Isostacy • Regional continental uplift Glaciation • Global (glacieustatic) Greenhouse Effect • Expansion of water at higher T Tectonic activity • Displacement due to mid-oceanic ridges, or Continental Flood Basalts (tectonoeustatic) • Increased sedimentation due to continental uplift • Breakup of super continents, creation of less dense Oceanic crust Modern Sea Level Rise Various Projections • • • • 18-60cm by 2050, 24-108cm by 2080 (Gornitz) 100yr storm flood could be reduced to 19-68yr by 2050, 4-60yr by 2080 Rates of Beach Erosion will increase 3-6 times by 2050, 4-8 times by 2080 9-88cm by 2100, 12m in the next 1000 years (Nichols) Once lost, a return to present atmospheric conditions will NOT be adequate to regenerate modern ice sheets Consequences • • • • Loss of property and coastal habitats Flood risk and potential loss of life Loss of renewable/subsistence resources Loss of Tourism, Recreation and Transportation Functions • Loss of non-monetary cultural resources • Loss in agriculture/aquaculture Canada Susceptibility Map based on 7 attributes • Geology • Modern rate of sea level rise • Coastal type • Relief • Tidal range • Wave energy • Modern rates of erosion Eg. A highly sensitive area has low relief, a high rising sea level already, a high tidal range, high tidal energy, high rates of erosion today, and is composed of beaches or marshes • High Risk: Atlantic Canada, the Beaufort Sea and the Frazer Delta What can we do? • A mitigated sea level rise is likely to be less devastating • Correlation with paleo-sea level and atmospheric CO2 is observed but direct consequence of burning of hydrocarbons uncertain Bibliography • Couch S, Gornitz V, 2002. Impacts of Sea Level Rise in the New York City Metropolitan Area. Global and Planetary Change. 32: 61-88 • Hallam A, Wignall P, 1999. Mass Extinctions and Sea Level Changes. Earths-Science Reviews. 48:217-250 • Herrmann A, Huapt B, Patzkowsky M, Seidov D, Slingerland R, 2004. Response of late Ordovician Paleoceanography to changes in sea level, continental drif, and atmospheric pCO2: otential cases for longterm cooling and glaciation. Paleo 210:385-401 • Hitz S, Smith J, 2004. Estimating Global Impacts from climate change. Global and Environmental Change. 14:201-218 • Leeder M, 2003. Sedimentology and Sedimentary Basins: From Turbulence to Tectonics. Blackwell, pp 258-266 • Monroe J, Wicander R, 2004. Historical Geology. Edited by Dodson K. Thomson Brooks/Cole, pp192, 213, 335 • Nicholls R, Lowe J, 2004. Benefits of Mitigation of climate change for coastal areas. Global and Environmental Change. 14:229244 • UNEP-www.grida.no/climate/vital/33.htm Thanks to John Shaw of the GSC for the swift and concise response to my email