* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dennis Anderson
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Decarbonisation measures in proposed UK electricity market reform wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Energiewende in Germany wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
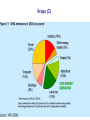
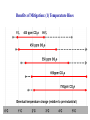
The Economics of Climate Change: Reflections on the Stern Report Dennis Anderson Imperial College Centre for Energy Policy and Technology (ICEPT) February 2007 Origins 1. Ministries of Finance Increasingly Engaged: a) b) c) d) Intervening in newly liberalised energy markets Taxing energy and pollution, financing R&D…. Effects on prices of Feed-in Tariffs, Obligations, Standards etc Effects on economic growth……… 2. Economists—many sceptical 3. Need to move beyond Kyoto—to involve US and developing countries especially 4. … and a sense that innovation offers a way forward Scope (1) 1. Approach: assumptions of ‘traditional’ cost-benefit analysis questioned: • • • • ethical precepts; limits of marginal analysis; uncertainties and risks; long-term nature of problem 2. Economic Impacts of Climate Change 3. Economics of Stabilization—benefits and costs 4. Policies for Mitigation 5. Policies for Adaptation 6. International collective action Scope (2) Benefits of Mitigation: (1) Temperature Rises Benefits of Mitigation: (2) Human and Physical Impact • • • • • • • • Falling crop yields in Africa Loss of glaciers and melt-water for irrigation in Asia Increased rates of run-off and flooding Extreme weather events Loss of Greenland Ice-cap Loss of Gulf Stream Intensification of greenhouse effect through thawing of permafrost ……… ……thought possible for some time ( ~ 2% probability in 2000) ……now thought likely—such scenarios are no longer ‘alarmist’ (recent estimate is > 50% probability at 3 ˚C) Benefits of Mitigation: (3) Raw Economic Effects Mitigation: estimating the costs 1. Estimate two emission trajectories • • Without policies in place (BAU) Trajectory to stabilise accumulations at 450—550 ppm 2. Compare costs of alternatives with fossil fuels 3. Examine alternative portfolios, bearing in mind constraints and energy system requirements 4. Allow for changes in income elasticities of demand 5. Calculate costs per ton of abatement 6. Add up the costs statistically (all the above are uncertain) Costs of Mitigation: (1) Emission Trajectories (2) Incremental Costs of Low Carbon Options as % Costs of Fossil Fuels (3) Portfolios considered. An example. • Above include hydrogen production for transport and dCHP • 20,000 ‘trials’ Using Monte Carlo Analysis (4) Changes in Income Elasticity (energy efficiency) Per Capita Income Elasticity of Energy Demand vs Per Capita Income 1.5 1 Is it moving downwards? Elasticity 0.5 0 -0.5 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 Per capita income (ppp, 1985 US$) Source: Plotted from Judson, Schmalensee and Stoker (1999). 10000 (5) Costs per ton of CO2 Abated Low oil and gas prices; lower rate of innovation High oil and gas prices; higher rate of innovation (6) Costs as % of World Product World product should grow by ~ 200% by 2050: • 125% in the OECD economies • 350% in the developing economies Climate Change Mitigation Policies 1. Carbon pricing—carbon taxes or tradable permits 2. Double R&D effort, which declined by 50% since 1974 3. 3-5 fold increase in finance for innovation over the next 10 years, from $35 billion/year today. Instruments: • • • 4. Feed-in tariffs Renewables obligations (transport and power) Tax incentives, grants and credits ….. Address ‘barriers’ to uptake of efficiency 5. Take up ‘win-win’ opportunities---remove fossil fuel subsidies; congestion pricing… 6. Above as basis for international co-operation, supported by CDM and Clean Energy Investment Facility of World Bank The Decline of the R&D Effort in the OECD 1974-present OECD: Million USD, 2004 prices and exchange rates 25,000 Other 20,000 Power & Storage technologies 15,000 Nuclear Fusion Nuclear Fission 10,000 Renewable Energy Fossil Fuels 5,000 Conservation 1974 1979 1984 1989 1994 1999 2004 Stern Report: Constructive and Optimistic (?) Economic growth 1000 EJ of output from ‘clean’ technologies 10 million MW of investment in electricity New international framework—linked to national policies Development of national policies 2007 Industry increasingly engaged Some policy experience over past 15 years Technological options proven and available—and not prohibitively expensive Science established, and reasonably conclusive