* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download July 02, 2011 |for Xavier`s College
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
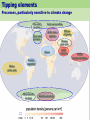
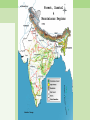
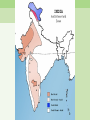
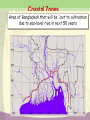
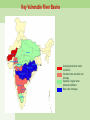
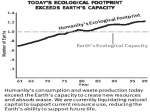
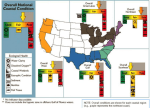
Climate Change Water stress, floods, ... Walter Mendoza mumbai xavier’s july 02, 2011 Key issues 350 ppm 2°C Disaster? Or Catastrophe? Tipping elements Processes, particularly sensitive to climate change Greenland ice sheet Deep water formation Arctic sea ice melting Arctic ozone depletion Himalaya snow cover Sahara Marine carbon cycle Amazon vegetation West Antarctic ice sheet Methane outgasing Antarctic ozone hole Indian monsoon El Niño Southern Oscillation Climate change and water • Superimposed on the existing crisis • Surface air temperature in India is going up at the rate of 0.4 degrees Centigrade • Rainfall patterns changing: more extreme rainy days; less number of rainy days; decline in summer rainfall • Total runoff in most rivers will increase, cause more flooding; runoff will be less in lean season Climate change and water • Glaciers melting at an accelerated rate, may cause increased flooding in Himalayan rivers and subsequent • Increase in flash floods • Glacier-fed rivers may eventually run dry Climate change and water • Rising sea levels and coastal erosion will gobble up land • Coastal freshwater aquifers turning saline • Large scale displacement • Increased extreme disasters (drought, floods, cyclones, etc) Health impact • As temperatures soar, humidity increases, as water becomes scarce, disasters such as floods increase, so will • Diarrhoea, cholera, malaria and other vector borne disease • Increased drought, leading to Poor water quality, dehydration, chronic low water consumption, poor sanitation and hygiene Social impact • Poor impacted the most, sustained poverty • Increased inequity • Affect on livelihood • Social unrest, increased conflicts Over the last 25 years, Gangotri glacier has retreated more than 850 meters Agriculture •Decrease in yield of crops as temperature increases in different parts of India - For example a a 2°C increase in mean air temperature, rice yields could decrease by about 0.75 ton/hectare in the high yield areas and by about 0.06 ton/hectare in the low yield coastal regions. •Major impacts of climate change will be on rain fed crops (other than rice and wheat), which account for nearly 60% of cropland area. In India poorest farmers practice rain fed agriculture. •The loss in farm-level net revenue will range between 9 and 25% for a temperature rise of 2-3.5°C. Coastal Zones •Simulation models show an increase in frequencies of tropical cyclones in the Bay of Bengal particularly intense events are projected during the post-monsoon period •Sea level rise is projected to displace populations in coastal zones, increase flooding in low-lying coastal areas, loss of crop yields from inundation and salinization. 7500 km coast line Vulnerable areas along the Indian Coast due to SLR Coastal Zones •Simulation models show an increase in frequencies of tropical cyclones in the Bay of Bengal particularly intense events are projected during the post-monsoon period •Sea level rise is projected to displace populations in coastal zones, increase flooding in low-lying coastal areas, loss of crop yields from inundation and salinization. 7500 km coast line Vulnerable areas along the Indian Coast due to SLR Key Vulnerable River Basins Acute physical water scarce conditions Constant water scarcities and shortage Seasonal / regular water stressed conditions Rare water shortages Health Malaria is likely to persist in many states and new regions at hogher latitudes may become malaria-prone The duration of the malaria transmission windows is likely to widen in northern and western states and shorten in southern states. Endemic regions of malaria Regions likely to be affected by malaria in 2050s Responses • NAPCC – National Action Plan on Climate Change - Water Mission • State Action Plans National Water Mission • Studies on Management of Water Resources • Management & regulation of Groundwater resources – Mandating water-harvesting and artificial recharge – Enhancing recharge of deep zones of aquifers – Mandatory water assessments and audits for industrial waste disposal – Regulation of power tariffs for irrigation Responses • NAPCC – National Action Plan on Climate Change - Water Mission • State Action Plans Responses • NAPCC – National Action Plan on Climate Change - Water Mission • State Action Plans National Water Mission (contd.) • Upgradation of storage systems for freshwater & drainage systems for wastewater – – – – Prioritizing vulnerable watersheds Rejuvenation of old water tanks Models for urban storm water flows Strengthen links with afforestation & wetland conservation – Enhance storage capacities in hydro projects • Conservation of wetlands • Development of Desalination techniques Responses Responses Responses mumbai mumbai Mithi river