* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Fossil fuel phase-out wikipedia , lookup
Energiewende in Germany wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Decarbonisation measures in proposed UK electricity market reform wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
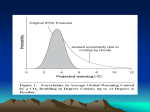
Climate Change: A Northwest Perspective Peggy Duxbury Seattle City Light February 20, 2008 Climate Change: A Northwest perspective • Most hydro-dependent region = most affected by climate change impacts • Allocation Matters! • NW Leadership on conservation and renewables should be recognized • NW utilities spend billions on salmon recovery, habitat protection, FERC relicensing to keep hydro operating Seattle Times, Nov 1, 2006 Power plant CO2 emissions Power plants in the Northwest generate 1% of national power plant CO2 emissions 99% 1% U.S. Power Plants The size of each circle represents the quantity of emissions in 2002 24 million tons 15 million tons 4.0 million tons Primary Fuel Type And 4% of national power output Coal = Black 96% Oil or Diesel = Blue Natural Gas = Red 4% LOWEST EMISSION RATES IN US (lbs of CO2 per mwh of electricity produced) 2,000 lbs/MWh 1,500 lbs/MWh 1,000 lbs/MWh Northwest Efficiency Achievements 1978 – 2005 3,500 Since 1978 Utility & BPA Programs, Energy Codes & Federal Efficiency Standards Have Produced Over 3100 aMW of Savings. Average Megawatts 3,000 2,500 2,000 1,500 1,000 500 0 1978 1982 BPA and Utility Programs 1986 1990 Alliance Programs 1994 State Codes 1998 2002 Federal Standards SOURCE: NW Power and Conservation Council, 2007 Allocation Comparison: Output vs. Emission Source: EIA 2004 & 2005 Difference between emission and performance/output approach @ $5/ton = $479 million @ $7/ton = $671 million @ $10/ton = $959 million Avoided Emissions from NW conservation (compared to coal) *CO2 allowance allocation based on total electricity output, including fossil, renewable, and incremental nuclear output (relative to 1990). Many still do little / no conservation: “In most of the11 state where AEP operates, it’s under no obligation to hold down demand. On the contrary, it makes more money the more electricity people use.” Source: “Inside the Messy Reality of Cutting Power Plant’s CO2 Output” Wall Street Journal, Thursday, July 12, 2007 Comparison of Emission-Based Allocation To Top Ten Emitting Utilities v NW States CO2 levels had 3,100 MW of conservation been coal-fired generation Tons *Utility allowance allocation based on 2004 data reported in Ceres, Natural Resource Defense Council, and Public Service Enterprise Group, Benchmarking Air Emissions of the 100 Largest Electric Power Producers in the United States 2004, (April 2006). State allowance allocation based on 2004 and 2005 EIA data. Emission-Based Give Many Allowances to Few Source: “Benchmarking Air Emissions of the 100 Largest Electric Generation Owners -2004” 100% 400,000,000 all others 350,000,000 CO2 based allocation Output based allocation Load based allocation (electricity sales) 100 largest producers 75% 300,000,000 250,000,000 50 producers 200,000,000 ( 50% 150,000,000 100,000,000 25% 18 producers FPL DTE Energy E.ON Texas Genco LLC First Energy Allegheny Energy AES 50,000,000 Tons 0 6 producers NM 0% MidAmerican Dominion Edison International Progress Energy TXU UT AEP Southern DukeOR TVA Xcel AZ Ameren WA CA 6-state region *CO2 allowance allocation based on total electricity output, including fossil, renewable, and incremental nuclear output (relative to 1990). Energy Efficiency Scorecard Highest ranking states: VT, CT, CA, MA, OR, WA, NY, NJ, RI 6 21 50 9 5 25 48 12 49 18 1 27 23 41 13 35 15 34 44 24 11 46 45 33 26 41 27 35 43 35 38 30 30 49 46 38 40 15 29 Maine 15 New Hampshire 18 Vermont 1 Massachusetts 4 Rhode Island 9 Connecticut 1 New York 7 Pennsylvania 14 New Jersey 8 Delaware 30 Maryland 20 Dist. Columbia 22 Lowest ranking states (number higher due to ties): ND, WY, MS, SD, AL, MO, AR, OK, TN, AK, IN, LA, GA, VA, KY, WV, NE Source: The State Energy Efficiency Scorecard for 2006, ACEEE, June, 2007 Regional and State Climate Initiatives Western Regional Climate Action Initiative Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative AB 32 Maryland District of Columbia Maine New Hampshire Vermont Massachusetts Rhode Island Connecticut New York California motor vehicle CO2 emissions standards RPS requirement or goal Pennsylvania New Jersey Delaware Florida GHG target CONCLUSION • Hydro most impacted power system from climate change • Allocation matters! • Emission-based allocation: – Disadvantages the NW – Rewards behavior we should discourage • NW leadership should be recognized