* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 - Levels of Organization
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
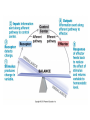
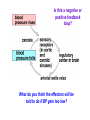
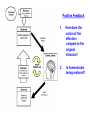
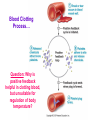
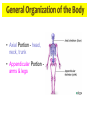
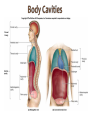
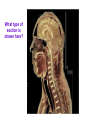
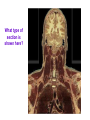
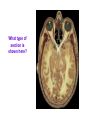
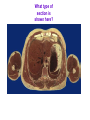
Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Physiology: The study of function How are they related? A body structure is specifically adapted for its function. Ex: the hand grasps while the heart pumps blood. What characteristics make you a living thing? How do we know you are alive? Characteristics of Life 1. Movement • Walking, endo/exocytosis, heart beat 2. Responsiveness • Reaction to a stimulus internal/external 3. Growth • Increase in body/cell size; cell material or cell number • Mitosis (repair/replace), meiosis, a new life 4. Reproduction 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Respiration Digestion Absorption Circulation Assimilation 10. Excretion • • • • • Obtaining oxygen and releasing energy from foods Breakdown of food substances. (catabolic) Moving through membranes. Moving within body fluids. (blood or lymph) Changing absorbed foods into other chemical structures. (anabolic) • Removing wastes from metabolic reactions. Everyday example using the characteristics of life… • • • • • • • I am walking to In and Out Burger (movement) I stop at the traffic light (response) My body is growing because I am young (growth) I am breathing air (respiration) I eat a Double-Double (digestion) My body absorbs the hamburger (absorption) The hamburger nutrients circulate in my blood (circulation) • The hamburger is changed to things my body needs (assimilation) • Eventually, I go to the bathroom (excretion) • I picked a scab that wasn’t ready. (reproduction) Metabolism: • All the physical and chemical changes. • All the body processes that use energy to function. • It is your engine! The speed of your engine is regulated by all the characteristics. What environmental requirements must be met so that you can stay alive? Environmental Requirements 1. Water 2. Food 3. Oxygen 4. Heat 5. Pressure • Solvent for reactions, transport, temperature regulation. • Building material, energy, enzymes • Releases energy from foods. • Regulates speed of metabolism/reactions. • Force needed for breathing and blood circulation. What is HOMEOSTASIS? Physiological principle that systems strive to maintain relatively constant internal environment. It is a balancing act! Adaptations to sudden or gradual changes must be met! Homeostasis usually operates to keep vital stats within a narrow range for normal function. Ex: Normal pH of blood is about 7.4 pH of 6.7 or 8.0 would mean death! Homeostasis control is mainly by the nervous and endocrine systems. What can cause homeostasis to become unbalanced? • Age, diet, stress, disease or disorders. How does Homeostasis work? 1. Receptors – messengers that pick up imbalance; send info to control center. 2. Control Center – interprets and sends out a response 3. Effectors – carries out response 4. Set Point – ideal internal value 5. Negative Feedback - process to return set point to normal. (Effectors cause an opposite response to stimulus; stimulus is reduced.) 6. Positive Feedback – stimulus is increased or reinforced by the effectors. Not very common. Is this an example of negative or positive feedback? Is this a negative or positive feedback loop? What do you think the effectors will be told to do if BP gets too low? Positive Feedback 1. How does the action of the effectors compare to the original stimulus? 2. Is homeostasis being restored? Blood Clotting Process… Question: Why is positive feedback helpful in clotting blood, but unsuitable for regulation of body temperature? What are the control centers? Effectors? • During lactation (milk production), the suckling by the baby stimulates the production of oxytocin, which in turn causes contraction of smooth muscle surrounding the milk duct, causing milk to flow. The flow of milk increases the suckling by the baby and more oxytocin is produced. Is this negative or positive feedback loop? • When blood glucose levels rise above a set point after eating a meal high in carbohydrates, beta cells in the pancreas are activated and release insulin into the blood. Insulin causes an increase in glucose uptake by body cells and causes the liver to take in glucose and convert it to glycogen. As a result, blood glucose levels decline to the set point. 1. Is this a negative or positive feedback loop? 2. What is the control center? 3. What is the effector? How is the body organized? Levels of Organization • Smallest to largest: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Atoms Molecules Macromolecules Organelles Cells Tissues Organs Systems Organism How would you order these? osteocyte calcium femur bone tissue skeleton Organ Systems 1. Body Covering 2. Support/Movement 3. Integration/Coordination 4. Transport 5. Absorption/Excretion 6. Reproduction • Integumentary • Skeletal, Muscular • Nervous, Endocrine • Cardiovascular, Lymphatic • Digestive, Respiratory, Urinary • Reproductive • Axial Portion - head, neck, trunk • Appendicular Portion arms & legs Dorsal Cavity Body Membranes Serous membranes line and cover cavities and organs. Two layers with a serous fluid for lubrication. 1. Parietal – membrane attached to the wall of a cavity. Lines the cavity the organ is in. 2. Visceral – membrane that covers an organ. These terms are further associated with: – Pleura – lungs – Pericardium – heart – Peritoneum - abdomen Body Regions How are the location of body parts described in relative to another body part? Must refer to correct ANATOMICAL POSITION Positional Terms • • • • • • • Superior – toward the top or head region Inferior – toward the bottom or feet Anterior or Ventral – front side Posterior or Dorsal – back side Medial – closer to midline Lateral – farther from midline Proximal – body part is closer to the point of limb attachment than other body part • Distal – body part farther from the point of limb attachment than other body part • Superficial – closer to the surface • Deep – deeper in the body Coronal Plane (front/back) Sagittal plane (right/left) (top/bottom) What type of section is shown here? What type of section is shown here? What type of section is shown here? What type of section is shown here?