* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Substances
Calorie restriction wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Malnutrition in South Africa wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Raw feeding wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
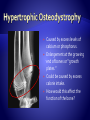
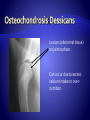
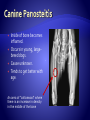
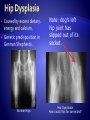
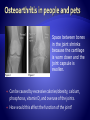
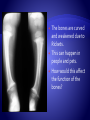
Copyright 2010. PEER.tamu.edu Protein Fat Carbohydrates Minerals Calcium Phosphorous Magnesium Vitamins Vitamin D Organic Inorganic What are some differences in these two substances? Can you guess what might make something organic or inorganic? Organic Substances are considered to come from biotic or living things, or things that were once alive. They contain Carbon. They typically also contain elements like hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. Inorganic substances are considered to come from abiotic or non-living materials. Many are minerals. Most do not contain Carbon. The Nutrients that affect Bones: Essential for muscle development . Muscle activity promotes bone development. Meat Fish Beans Too much fat = BAD! A diet needs to be balanced for optimum health. Obesity results in excessive weight & pressure on bones – not to mention the other problems of obesity. This is one fat dog! It’s excess weight puts its bones in danger. Energy! Excess energy comes in highcarbohydrate diets or excessive food intake. Excess dietary carbohydrate leads to excess calories in diet. Excess calories can lead to obesity! Major component of bone. Has to be in balance with Phosphorus. Not all forms of calcium are equally absorbed from the digestive system. Vitamin D promotes absorption. Milk is a great source Of Calcium Regulates balance with calcium. Too much phosphorus can decrease bone density. Diets with excess phosphorous can decrease calcium absorption. Some sodas have large amounts of phosphorus and this can lead to calcium imbalance and a decrease in bone density. http://www.webmd.com/osteoporosis/feat ures/soda-osteoporosis Important for bone and tooth structure. Spinach is a good source of Magnesium Regulates digestive system absorption, excretion, & balance of calcium and phosphorus. Required in dog and cat diets! Humans make vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, dogs and cats cannot. During skeletal development, building of bone is dependent on how much calcium and phosphorus in is the diet and their proper regulation. Added to most milk! What are the nutrients involved with bone development? What is the difference between Organic and Inorganic? Why are excess carbohydrates or excess fats harmful to bones? If people’s or pets’ diets are not balanced, many problems in bones can develop. Malnutrition (not enough of the required nutrients), or over-nutrition (too much of the required nutrients) are both dangerous. Imbalances in calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D intake directly affect bones. All growing puppies can be harmed by dietary imbalances and excessive food intake. Malnutrition can especially cause problems in large-breed dogs. Why do you think that is? Can you see abnormalities (problems) in the radiographs on the following slides? A radiograph is a picture made by using x-rays. Caused by excess levels of calcium or phosphorus. Enlargement at the growing end of bones or “growth plates.” Could be caused by excess calorie intake. How would this affect the function of the bone? Lesions (abnormal tissue) on joint surface . Can occur due to excess calcium intake or overnutrition. Inside of bone becomes inflamed. Occurs in young, largebreed dogs. Cause unknown. Tends to get better with age. An area of "cottonwool“ where there is an increase in density in the middle of the bone Caused by excess dietary. energy and calcium. Genetic predisposition in German Shepherds. Normal Hips Note: dog’s left hip joint has slipped out of its socket. Hip Dysplasia How could this be corrected? Space between bones in the joint shrinks because the cartilage is worn down and the joint capsule is swollen. Can be caused by excessive calories/obesity, calcium, phosphorus, vitamin D, and overuse of the joints. How would this affect the function of the joint? Rickets is a disease that causes deformity of bones, especially the bones of the spine, ribs, and legs. The disease can result in knock knees, bow legs, painful spasms, and difficulty breathing. Rickets was common in Europe and North America until the early 1900’s. Ancient Chinese, Egyptian, Greek, and Roman physicians knew of the disease. The major cause of rickets is a lack of Vitamin D. The bones are curved and weakened due to Rickets. This can happen in people and pets. How would this affect the function of the bones? What are some of the conditions that affect bones that can be caused by imbalances in the diet? What is Rickets and what is it caused by? It is extremely important, especially at your age, to get the proper nutrients in the right amounts necessary for bone growth and strength!