* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Staying Alive Powerpoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
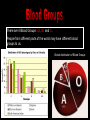
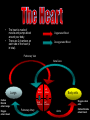
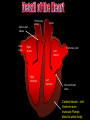
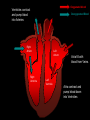
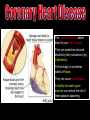
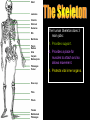
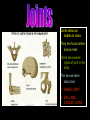
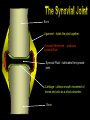
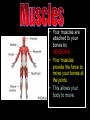
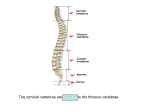
S2 Biology Madras College • When you exercise, your heart beats faster and you breathe quicker and more deeply. • This provides your muscles with more oxygen and sugar from your blood. • The Oxygen and Sugar are needed by your muscle cells for RESPIRATION. • The main jobs of the blood are: – Transport Oxygen and Food to your body cells. – Removal of Carbon Dioxide and Waste Chemicals from your cells. – Protection from Disease. Plasma – Liquid part of blood. Contains cells and dissolved substances. Red Blood Cell – Contain Haemoglobin and carry Oxygen. Platelets – Help blood to clot. White Blood Cell – Helps destroy infecting germs. There are 4 Blood Groups A,B,AB and O. People from different parts of the world may have different blood groups to us. Global distribution of Blood Groups • • The heart is made of muscle and pumps blood around your body. There are 2 chambers on each side of the heart (4 in total). Oxygenated Blood Deoxygenated Blood Pulmonary Vein Vena Cava Lungs Carbon Dioxide enters lungs. Oxygen enters blood Pulmonary Artery Right Atrium Left Atrium Right Ventricle Left Ventricle Body cells Oxygen enters cells. Aorta Carbon Dioxide enters blood. Pulmonary Artery Semi-Lunar Valves Vena Cava Aorta Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle Pulmonary Vein Atrioventricular Valve Cardiac Muscle – Left Ventricle more muscular. Pumps blood to whole body. Oxygenated blood Ventricles contract and pump blood into Arteries Deoxygenated Blood Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle Atria fill with blood from Veins. Atria contract and pump blood down into Ventricles • You can listen to your heart beat with a stethoscope. • There are 3 types of blood vessel. • These are Arteries, Veins and Capillaries. Thick muscular wall. Thin walls. Walls ONE CELL thick. Carry blood AWAY from heart. Carry blood TO the heart. Substances exchanged between BLOOD and CELLS. Blood under HIGH PRESSURE. Blood under LOW PRESSURE. Have VALVES. Deliver blood to ALL BODY CELLS. The Coronary Arteries deliver blood to your heart muscle. They can sometimes become blocked by fatty substances (eg. Cholesterol). The blockage is sometimes called a Plaque. They can cause heart attacks. A healthy diet and regular exercise can reduce the risk of these plaques appearing. Causes of heart attacks are written inside the heart. Good advice is written outside. Remember: Skull Jawbone Clavicle Sternum Humerus Rib The human Skeleton does 3 main jobs: Backbone Pelvis Radius Ulna Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Knee cap Tibia Fibula Tarsals Metatarsals Phalanges 1. Provides support . 2. Provides a place for muscles to attach and so allows movement. 3. Protects vital inner organs. Joints allow our bodies to move. They are found where bones meet. There are several types of joint in the body. The two we learn about are: 1. HINGE JOINT. 2. BALL AND SOCKET JOINT. • Hinge joints (eg. Finger, knee, elbow) only move in 1 direction • These joints (eg. Hip, Shoulder joint) can move in many directions Bone Ligament – holds the joint together. Synovial Membrane – produces synovial fluid. Synovial Fluid – lubricates the synovial joint. Cartilage – allows smooth movement of bones and acts as a shock absorber. Bone • Your muscles are attached to your bones by TENDONS. • Your muscles provide the force to move your bones at the joints. • This allows your body to move. • Muscles can only.. • CONTRACT – Become shorter. • RELAX – Become longer. RELAX CONTRACT Muscles work in pairs. Eg. BICEPS and TRICEPS in the upper arm. When one contracts, the other relaxes. Muscles which work this way are ANTAGONISTIC. Biceps relax. Biceps contract. Triceps contract. Triceps relax. Arm lowered. Arm raised. BICEPS • Muscles and Bones work like LEVERS. LOAD EFFORT 1 Kg PIVOT TENDONS join MUSCLE to BONE. BONE LIGAMENTS join BONE to BONE. LIGAMENTS BONE BONE TENDONS