* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Health Science Education
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Toxocariasis wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Toxoplasmosis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Brugia malayi wikipedia , lookup
Hookworm infection wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Fasciolosis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
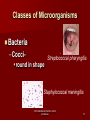
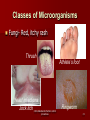
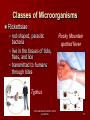
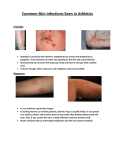
Unit A 2.02 Principles of Infection 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 1 Types of Infections 2.02 Understand infection control procedures Types of Infections Infection invasion of the body by microorganisms or pathogens invading microorganisms: – use the host’s resources to multiply – interfere with normal function – 3rd leading cause of death in the U. S. 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 3 Types of Infections VERY IMPORTANT Any sign of infection must be reported to the nurse or doctor! 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 4 Types of Infections Local infection only a specific portion of the body is infected – pain – redness – heat at the site – swelling – pus – foul smelling drainage 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 5 Types of Infections Systemic infection affects the entire body – fever – aches – chills – nausea – vomiting – weakness 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 6 Types of Infections Endogenous (endo- inside; genous- type or kind) – type or kind of infection or disease that originates from within the body Exogenous (exo- outside; genous- type or kind) – type or kind of infection or disease that originates outside the body 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 7 Types of Infections Nosocomial infections – Hospital acquired infection – Transmitted by the health care worker Opportunistic infections – Infections that occur when the body’s defenses are weakened 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 8 Types of Infections VERY IMPORTANT Any sign of infection must be reported to the nurse or doctor! 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 9 Classes of Microorganisms 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 10 Classes of Microorganisms Non-pathogenic – normal – do not produce disease – beneficial Pathogenic – cause infection and disease May be non-pathogenic in one body system, pathogenic in another (E. coli) 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 11 Classes of Microorganisms Aerobic – requires oxygen to live Anaerobic – does not require oxygen to live 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 12 Classes of Microorganisms 6 classes of microorganisms – Bacteria – Protozoa – Fungi – Rickettsiae – Viruses – Helminths 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 13 Classes of Microorganisms Bacteria Often considered the causes of disease Certain bacteria – produce antibiotics – live in the body without problems – live on the roots of certain plants, converting nitrogen into a usable form – help break down dead organic matter Classified by shape and arrangement Treated with antibiotics 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 14 Classes of Microorganisms Bacteria –Cocci round in shape Streptococcal pharyngitis Staphylococcal meningitis 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 15 Classes of Microorganisms Bacteria –Bacilli rod shape Escherichia coli (E. coli) 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 16 Classes of Microorganisms Bacteria Cholera –Spirilla spiral or corkscrew shape Spirochete Lyme disease 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 17 Classes of Microorganisms Bacteria Some bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics Very difficult to cure – Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus (MRSA) – Multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus (MDSA) 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 18 Classes of Microorganisms Protozoa – One celled, animal-like organism – Contain a nucleus and other defined organelles Malaria African sleeping sickness Protozoa 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 19 Classes of Microorganisms Fungi – organisms that usually enjoy a symbiotic, but sometimes parasitic relationship with their host – provide numerous drugs and foods – provide bubbles in bread, champagne, and beer – cause a number of plant and animal diseases – fungal diseases are very difficult to treat 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 20 Classes of Microorganisms Fungi- Red, itchy rash Thrush Athlete’s foot Yeast infections Jock itch 2.02 Understand infection control procedures Ringworm 21 Classes of Microorganisms Rickettsiae – rod-shaped, parasitic bacteria – live in the tissues of ticks, fleas, and lice – transmitted to humans through bites Rocky Mountain spotted fever Typhus 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 22 Classes of Microorganisms Hepatitis virus Viruses – small, infectious agent – requires a host for survival – over 5,000 types – can combine in multiple ways to produce a wide range of diseases – produce immune response in humans – treated with antiviral drugs Influenza 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 23 Classes of Microorganisms Helminths – – – – – – Parasitic worm-like organisms Live inside the host Feed off their host Disrupt nutrient absorption Lead to weakness Excrete toxins making host susceptible to other diseases – Approximately 30 billion people globally are infected 2.02 Understand infection control procedures Pinworm Tapeworm 24 Classes of Microorganisms Bacteria Protozoa Fungi Rickettsiae Viruses Helminths 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 25 2.02 Transmitting Infection Transmitting Infection Direct contact Indirect contact Airborne Vector-borne 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 27 Transmitting Infection Direct contact Person to person (Physical or sexual) Animal to person Mother to unborn child 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 28 Transmitting Infection Indirect contact Pathogens are passed along on inanimate objects in the environment Fomites 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 29 Transmitting Infection Airborne Pathogens are carried through the air Cling to surroundings and are spread 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 30 Transmitting Infection Vector-borne Insects carry pathogen from host to host Rodents, small animals Flea Mosquito Tick 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 31 Transmitting Infection How you get an infection… – Causative agent – Reservoir – Portal of exit – Mode of transmission – Portal of entry – Susceptible host…breaking the chain! 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 32 Chain of Infection Causative agent Source or reservoir Susceptible host Portal of entry Portal of exit Mode of transmission 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 33 Chain of Infection Causative agent – pathogen 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 34 Chain of Infection Reservoir – area where the pathogen can live 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 35 Chain of Infection Portal of exit – way for the pathogen to escape from the reservoir 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 36 Chain of Infection Mode of transmission – way for pathogen to be transmitted 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 37 Chain of Infection Portal of entry – way to enter new reservoir 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 38 Chain of Infection Susceptible host – able to be affected – person likely to get sick 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 39 Chain of Infection Causative agent Source or reservoir Susceptible host Portal of entry Portal of exit Mode of transmission 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 40 Chain of Infection 2.02 Understand infection control procedures 41