* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download V3ch11b - SchultzMedic
Hookworm infection wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Infectious mononucleosis wikipedia , lookup
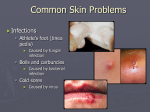
Mononucleosis Viral Infection Symptoms Caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) Transmitted through oropharyngeal contact Fatigue, followed by fever, severe sore throat, oral discharges, and enlarged, tender lymph nodes Management Herpes Viral Infection Transmitted in saliva and commonly infects the oropharynx, face, lips, skin, fingers, and toes Symptoms Simplex Virus Type 1 Fluid-filled vesicles that develop into cold sores or fever blisters, then small ulcerations Fever, malaise, and dehydration may occur also. Management Epiglottitis Inflammation of the Epiglottis True emergency in children Characteristics Dysphonia, drooling, dysphagia, distress Stridor, fever, sore throat Croup Viral Illness Causing Upper-Airway Obstruction Characteristics Stridor, “seal-bark” cough, nocturnal occurrence with acute distress, tachypnea, and retractions Pharyngitis Infection of the Pharynx and Tonsils Characteristics Sudden onset of sore throat and fever, with swelling of the palate, tonsils, and lymph nodes Common in 5- to 11-year-old patients Scarlet fever Sinusitis Infection of the Paranasal Sinuses Characteristics Purulent or blood-tinged drainage Congestion and pressure Hantavirus Viral Infection Carried by Rodents Characteristics Fatigue, fever, aches, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain Severe myocardial depression Gastroenteritis Characteristics Pathogens Nausea, vomiting, cramping or discomfort, anorexia, and diarrhea Causes include viruses, bacteria, and parasites Risks include age, international travel, contaminated food and water supply Management Food Characteristics Poisoning Diarrhea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal distress Pathogens Commonly bacterial infections E. coli O157:H7 Often found in undercooked meat Produces a potent neurotoxin Management © Phototake NYC Encephalitis Infection of the Brain Clinical Presentation Typically viral in nature Commonly co-exists with meningitis Decreased level of consciousness, fever, headache, drowsiness, coma, tremors, and stiff neck/back Management Rabies Viral Infection Affecting the Nervous System Transmitted through bites, nonintact skin, and direct contact with a mucous membrane Symptoms Prodromes Malaise, headache, fever, chills, sore throat, myalgias, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea Encephalitic phase Excessive motor activity, excitation, and agitation Management Inspect and irrigate wound Do not bandage; allow the wound to drain Notify appropriate authorities so source animal’s status can be determined Perform post-exposure prophylaxis Immunization © Getty Images, Inc.—Stone Allstock Tetanus Bacterial Infection of the CNS Symptoms Infection often occurs in minor wounds and burns Rigidity of muscles occurs close to infection site Generalized symptoms include pain and stiffness in the jaw, muscle spasms, and respiratory arrest Management Immunization Lyme Inflammatory Disorder Caused by a tick-borne spirochete Stages of Disease Early localized “Bull’s eye” rash Early disseminated Spirochete spreads to the skin, nervous system, heart, and joints Late Disease Encephalopathy with cognitive deficits, depression, and sleep disorders Management Immunization Gonorrhea Gram-Negative Bacterial Infection Symptoms Transmitted by direct sexual contact with infected partner Local Systemic Management © Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Syphilis Bloodborne Infection Stages of Syphilis Caused by spirochete Transmitted by sexual intercourse or direct contact with a lesion Primary Secondary Latent Tertiary Management © Bookside Associates, Ltd. Genital Viral Infection Warts Highly contagious Transmitted by contact Symptoms Cauliflower-like, fleshy growths on the penis, anus, labial surfaces, and anal mucosa © Photo Researchers, Inc. Herpes Viral Infection Transmitted by sexual contact Characteristics Simplex Type 2 Vesicular lesions on penis, anus, rectum, mouth, vulva, buttocks, legs, and perineum Lesions that heal but occur throughout the patient’s lifetime Management © Photo Researchers, Inc. Chlamydia Parasitic Infection Characteristics Transmitted by sexual activity and hand-to-hand contact of eye secretions Similar to gonorrhea May cause blindness, sterility Management Trichomoniasis Protozoan Parasite Infection Characteristics Transmitted by sexual contact Males usually asymptomatic carriers Vaginal discharge, irritation of the perineum and thighs, and dysuria Often concurrent with gonorrhea Management Chancroid Highly Contagious Bacterial Ulcer Characteristics Transmitted by direct sexual contact Painful, inflamed pustule or ulcer that may appear on the penis, anus, urethra, or vulva Management © Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Impetigo Bacterial Infection Highly contagious Spread by direct contact Caused by staphylococci or streptococci Lesions most commonly occur on the extremities and joints Standard precautions Lice Parasitic Infestation Commonly occurs on the scalp, trunk, or pubic areas Repeated infestations may cause an allergic response Treatment Scabies Mite Infestation Characterized by intense itching Remove and decontaminate any clothing that may have contacted the patient Scabicides © Phototake NYC Infection Occurring in Hospitalized Patients Pathogens Often include antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections: Vancomycin-resistant enterococcus (VRE) Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSE) Tuberculosis Role Recognize: of the Paramedic The history of sensationalized or misunderstood media coverage of infectious disease outbreaks The significance of leading by example The serious personal and public health implications of infectious disease Educate the public: Introduce disease transmission as part of CPR and first aid classes Personal Ensure personal health Do not work if you have diarrhea, a draining wound, mononucleosis, or a cold; have untreated lice, scabies, or strep throat; or are jaundiced. Maintain current immunizations Accountability MMR, hepatitis B, DPT, polio, chickenpox, influenza, and rabies (if appropriate) Utilize BSI, PPE, and infection control materials Keep your education current Public Health Principles and Agencies Microorganisms Contraction, Transmission, and Stages of Disease The Body’s Defenses against Disease Infection Control in Prehospital Care Assessment of the Patient with Infectious Disease Selected Infectious Diseases Patient Education Preventing Disease Transmission