* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 20.3
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Lyme disease microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
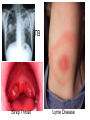
20.3 Bacterial & Viral Diseases pg 586-592 Pathogen- microorganisms that cause disease 2 ways: 1. destroy living cells; tuberculosisdestroys lung tissue 2. releases a chemical that upsets homeostasis; diphtheria, botulism Louis Pasteur Germ Theory of Disease 1800’s Bacterial Diseases: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. TB Diptheria Lyme Disease Tetanus Strep Throat (Bacterial) Meningitis TB Strep Throat Lyme Disease Vector? Risk Map Type of Bacteria? Tetanus Control Disease 5 ways to control1. physical removal 2. disinfectants 3. proper food storage 4. proper food processing 5. sterilization by heat Vaccines weakened or killed pathogen or inactivated toxin (usually for viral diseases) (prevention) Antibiotics attack bacterial infection (treatment) Viruses -attack and destroy certain cells or cause infected cells to change patterns of growth and development Prevention of viral diseases -vaccines -personal hygiene -Cannot be treated with antibiotics, they only kill bacteria (few antiviral drugs) Viral Diseases: Common Cold Chicken Pox Influenza • Emerging diseases= unknown disease that appears in a population for the first time or a well known disease that suddenly becomes harder to control Little or no resistance to them, no methods of control yet. People travel much more, so easily spread. MRSA, West Nile, Ebola, SARS …….. Emerging Diseases – This map shows locations worldwide where specific emerging diseases have broken out in recent years. – In recent years, new diseases, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Asia, have appeared. At the same time, some diseases thought to be under control have come back. • Antibiotics kill off the bacteria with no resistance, leaving the resistant ones behind. These resistant bacteria reproduce. • = “Super Bugs” • Ex: MRSA “Superbugs” – An especially dangerous form of multiple drug resistance has recently appeared in a common bacterium. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, known as MRSA, can cause infections that are especially difficult to control. – MRSA skin infections can be spread by close contact, including the sharing of personal items such as athletic gear, and are especially dangerous in hospitals, where MRSA bacteria can infect surgical wounds and spread from patient to patient. Mad Cow Disease Mad Cow Disease • Prions— – Protein infectious particles: brain problem. Misfolded prion proteins cause normal prion proteins to misfold; they accumulate, cells are damaged and cease to function