* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Infectious Disease Committee, Woodbury County Definition
Foodborne illness wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
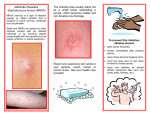
MRSA Fact Sheet: Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Prepared by: Infectious Disease Committee, Woodbury County Definition: Methicillin-Resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) is a type of Staphylococcus or “Staph” bacteria. Staph bacteria commonly live on the skin and in the nose and usually do not cause any harm. However, sometimes they cause infections. These infections are usually treated with antibiotics. When common antibiotics don’t kill the staph bacteria, it means the bacteria have become resistant to those antibiotics. This type of staph is called MRSA. Appearance: Ø Sores that look and feel like spider bites Ø Large, red painful bumps under the skin (boils) Ø A cut that is swollen, hot and filled with pus 1/3 MRSA Ø Blisters filled with fluid (impetigo) Treatment: Your healthcare provider will decide the best way to treat your infection. Treatment may include taking an antibiotic or having a doctor drain the infection. If you are given an antibiotic, be sure to take all the doses and do not share them with other people or save them to use later. Prevention: Ø Wash your hands often or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer Ø Keep your cuts and scrapes clean and cover them with bandages Ø Do not touch other people’s cuts or bandages Ø Do not share personal items like towels or razors 2/3 MRSA More Information: To access additional information please visit www.cdc.gov/MRSA or click here . 3/3