* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Male Reproductive System Key Terms
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
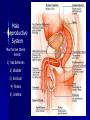
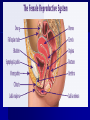
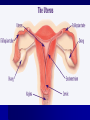
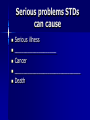
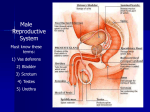
Male Reproductive System Must know these terms: 1) Vas deferens 2) Bladder 3) Scrotum 4) Testes 5) Urethra Male Reproductive System Key Terms Sperm-________________________ _______________________________ Semen- fluid made up of sperm & other secretions from the male reproductive organs Egg (ovum)- sex cell that is produced by the ovaries & that can be fertilized by sperm Fertilization- sperm & egg join to create a new human life Female Reproductive System Key Terms Ovary- female reproductive organ that _______________ _____________& the hormones estrogen & progesterone Vagina- female reproductive organ that connects the outside of the body to the uterus & receives sperm during reproduction Fallopian tubes- transports an egg from the ovary to the uterus Uterus- female reproductive organ that provides a place to support a developing human Urethra- The transport tube leading from the _____ ________ outside the body. In men is also carries semen. Menstrual cycle- monthly series of hormone-controlled changes that prepare the uterine lining for a pregnancy Menstrual Cycle (Period) Risk of Adolescent Sexual Activity Sexually Transmitted Diseases Key Terms Sexually transmitted disease (STD)- an infectious disease that is spread by sexual contact Epidemic- _____________________ _____________________________ Asymptomatic- showing no signs of a disease or disorder even though an infection or disease is present 2 Risks of Sexual Activity Unplanned pregnancey _______________________________ Statistics on Sexually Transmitted Diseases Abstinence Serious problems STDs can cause Serious illness ___________________ Cancer ______________________________ Death 4 High Risk Behaviors Puts Teens at Risk for STDs Being Sexually Active Having more than one ____________ Having a _______________________ _______________________________ Using alcohol or drugs Abstinence- the only 100% way to prevent unplanned pregnancy & STDs Preventing STDs 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Practice Abstinence Stay away from alcohol & drugs ________________________, & use those facts to make good decisions Choose friends who influence you in a positive way _______________________ 4 Ways STDs are Spread Any type of sexual activity that brings an uninfected person in contact with _______ from an infected person Any sexual activity that results in contact between one _______________________ __________________, in which one of the persons is already infected with an STD Direct contact with _______________ Mother to her baby before birth, during birth, or during breast feeding Babies & STDs Miscarriage ________________ – bacteria infects baby’s eyes as the baby passes through the birth canal – Antibiotic eye drops Common STDs Key Terms _________________- bacterial STD that infects the reproductive organs & that causes a mucous discharge __________________________- inflammation of the upper female reproductive tract that is caused by the migration of a bacterial infection from the vagina ________________- STD that is caused by a bacterium that infects mucous membranes, including the genital mucous membranes _________________- bacterial STD that causes ulcers or chancres; if untreated, it can lead to mental & physical disabilities & premature death _______________________- group of viruses that can cause genital warts in males & females & can cause cervical cancer in females Bacterial STDs Treatment- Antibiotics ________________ Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) _________________ Syphilis Chlamydia- bacterial STD that infects the reproductive organs & that causes a mucous discharge Symptoms -Pain during ____________ -Penis discharge & vaginal discharge & bleeding If untreated -Infertility -Pelvic pain -Pelvic Inflammatory Disease -_______________________ -blindness in infants Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)inflammation of the upper female reproductive tract that is caused by the migration of a bacterial infection from the vagina Symptoms – – – – – – Pain in abdoben/pelvic ___________________ Long & painful menstual cycles Painful urination Fever Nausea If untreated – _________________________ _________________________ – Chronic pelvic pain Gonorrhea- STD that is caused by a bacterium that infects mucous membranes, including the genital mucous membranes Symptoms – Painful urination – Discharge from penis & discharge or bleeding from vagina – Pain in pelvic area If untreated – ________________ – Scars urethra/painful urination – ________________________ – Blindness – Joint infection Syphilis- bacterial STD that causes ulcers or chancres; if untreated, it can lead to mental & physical disabilities & premature death Symptoms – Phase 1-painless ___________________ – Phase 2-fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, joint pain, muscle aches – Phase 3- __________________________, blindness, loss of mental abilities, death If Untreated – – – – Mental & physical disabilities ____________________ Severe mental disabilities Deafness Viral STDs No Cures _____________________________ Genital Herpes ________________ Human Immuno-deficiency Virus (HIV) Human Papiloma Virus (HPV)- group of viruses that can cause genital warts in males & females & can cause cervical cancer in females Symptoms – ______________________ Treatment – Surgical removal, freezing or medication for warts but will often return If untreated – ________________________ – Increased risk of developing genital cancers Genital Herpes Symptoms -Type 1- ________ _______________ -Type 2-mild or no symptoms If untreated – Infections of liver, brain, skin, eyes, & mouth – _________________ Hepatitis Hepatitis ___________ are STD’s Symptoms- tired, muscle aches, fever, loss of appetite, dark urine Treatment- ________________, vaccine for B If untreated- liver damage, failure, cancer, premature death STDs Caused by Parasites Pubic Lice-crawl on the skin & _________________, spread by skin to skin contact Scabies- ________________ _____________ of an infected person, skin to skin contact Trichomoniasis-protozoan, single celled animal that is little larger that a bacterium 5 things person should do if they think they have an STD 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) ____________________________ Complete the full course of medication Have follow-up testing done ______________________________ Notify all sexual partners