* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Immune System
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Lyme disease microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to viruses wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Social history of viruses wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
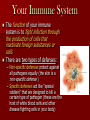
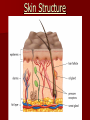
The Immune System Part I Physiology Standards: 10a-e Germ Theory and Non-specific defense The Germ Theory The germ theory states that: – infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms of different types, commonly called germs – Many believed that sickness and poor health was the work of ‘spirits’ or some ‘higher source’ A disease is any condition that disrupts the normal functioning of the body A pathogen usually “transmits” the disease to a host Salmonella is a bacterium found on and in all raw chicken! Agents of Disease There are many examples of agents for diseases and they fall into 5 major groups: – Viruses – the most common is influenza known as “the flu” – Bacteria – can either break down cells or release toxins into the organism – Protists – a disease that is often transmitted by an animal like malaria from mosquitoes – Worms – worms use humans as hosts while they act like parasites – Fungi – fungus causes infections in warm, moist places like athlete’s foot E. coli is a bacterium found in raw meat Agents of Disease Viruses vs. Bacteria – Both cause disease, but they act in different ways – Viruses: Take over a cell’s DNA and instruct the cell to “make” more viruses There is no “pill” to cure a virus, only the body can cure itself – Bacteria: Either destroy tissue or release poisonous toxins within your body causing illness You can take antibiotics to cure yourself of a bacterial infection Flu virus Agents of Disease Protists – single-celled animals – Protists often have a complex lifecycle where they take a couple of forms before infecting humans – Malaria attacks human red blood cells! Worms – the “tropical” parasite – Flatworms and roundworms are the cause of many diseases and severe discomfort – Ascaris is a dangerous and common roundworm while tapeworms are common flatworms Disease Transmission How do you get sick ? – What are three ways you can acquire a disease? What are the ways to prevent disease? – Name three things you can do daily to prevent catching a sickness. Your Immune System The function of your immune system is to fight infection through the production of cells that inactivate foreign substances or cells There are two types of defenses: – Non-specific defenses protect against all pathogens equally (the skin is a non-specific defense ) – Specific defenses act like “special soldiers” that are designed to kill a certain type of pathogen (these are the host of white blood cells and other disease fighting cells in your body) The Immune System Nonspecific Defense – your “general” defense system against pathogens – The skin is the most important line of defense against nearly all pathogens The skin is capable of secretions such as oil, mucus, saliva, and tears that create an intolerable environment for many pathogens Sweat is also a great defense against pathogens! Skin Structure