* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Applied Endocrinology
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gynecomastia wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Sexually dimorphic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal breast enhancement wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
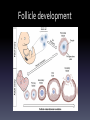
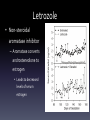
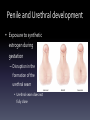
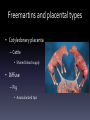
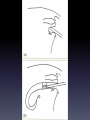
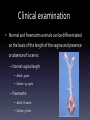
Applied Endocrinology Overview • Fetal growth retardation (FGR) caused by estrogen – Ovarian development – Hippocampal development – Penile and urethral tissue development • Freemartinism FGR- ovarian development • Follicular pool is established in utero • Placental estrogen levels increase with gestation • Estrogen regulates fetal ovarian follicle development Follicle development • Low serum estradiol levels – Can lead to a 50% decrease in growing follicles – Majority of the remaining follicles developing contain unhealthy oocytes • Lead to sub-fertility Letrozole • Non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor – Aromatase converts androstenedione to estrogen • Leads to decreased levels of serum estrogen Puberty and Postmenarche • Decreased serum estrogen levels during gestation – Delayed on set of puberty – Increased postmenarche cycle length • Letrozole treated animals showed a cycle that lasted six days longer Hippocampal Development • Hippocampus develops from the telencephalon • Important for learning and memory formation Hippocampal • Programmed for normal development and function by estrogen • Estrogen regulates development of synapse formation, long-term potential of the hippocampus, and a neuroprotective effect on stress Estrogen affects on Hippocampal • Disruption in hippocampal estrogen synthesis – Loss of spine synapse in hippocampus • Two main receptors: alpha and beta – Estrogen receptor alpha • Responsible for mediating estrogen through the direction of homodimer binding to estrogen – Homodimer binding is the binding of substrates to transcription factors to mediate the translation of DNA Fetal growth retardation • FGR causes estrogen levels in tissues of the hippocampal to decrease Male vs. Female development Male Female • FGR decreases the • No affect programming of estrogen and estrogen receptors in the hippocampal • Cause the hippocampal to not develop fully Penile and Urethral development • Exposure to synthetic estrogen during gestation – Disruption in the formation of the urethral seam • Urethral seam does not fully close • Hypospadias – Leads to difficult urination, ejaculation and sub-fertility • Urethral seam closure – Caused by apoptosis – Synthetic estrogen causes: • Apoptosis to be eliminated • Suppression of growth of the genital tubercle • Exposure of high estrogen – Only 36 hours • Affects development of penile and urethral tissue Freemartinism • Co-gestation of male and female – Male fetus develops sooner than female • Day 40- gonads begin to differentiate into testis – Testis (Sertoli cells) secrete anti-Müllerian hormone • Day 80- Leydig cells secrete testosterone – Stimulates the Wolffian duct system to develop into the epididymis and the vas deferens – Female fetus develops later in gestation • Day 60- uterine part of Müllerian duct starts to enlarge – Develops into the oviducts, uterus, cervix, and anterior vagina • Day 70- meiosis begins in the ovaries • Day 79- the Wolffian duct regresses • Common circulation of blood between male and female conceptuses • Anti-Müllerian hormone and testosterone present first – Exert effects on the female conceptus • Short, blind ending vagina • Posterior vagina normal because of development from perineal region Freemartins and placental types • Cotyledonary placenta – Cattle • Shared blood supply • Diffuse – Pig • Avascularized tips Freemartinism • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s2YFgvg Dd18 Clinical examination • Normal and freemartin animals can be differentiated on the basis of the length of the vagina and presence or absence of a cervix – Normal vaginal length • Adult- 30cm • Calves- 13-15cm – Freemartin • Adult- 8-10cm • Calves- 5-6cm • Use a blunt probe that is well lubricated • Insert at 45° angle below the horizontal for approximately two inches and then angle downward to avoid catching the hymen If time… • Distal hypospadias repair animation – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BqO8WxG- XvE References • Pepe, Gerald J., Terrie J. Lynch, and Eugene D. Albrecht. Regulation of Baboon Fetal Ovarian Development by Placental Estrogen: Onset of Puberty is Delayed in Offspring Deprived of Estrogen In Utero. Journal of Biology of Reproduction. 2013. 89(6); 123, 1-8. DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.112.107318 • Numpang, Ben. Xingrao Ke, Xing Yu, Christopher Callaway, Robert McKnight, Lisa Joss-Moore, and Robert Lane. Fetal growth restriction alters hippocampal 17-beta estradiol estrogen receptor alpha levels in the newborn male rat. Journal of Systems Biology in Reproductive Medicine. 2013. 59; 184-190. DOI: 10.3109/19396368.2013.786767 • Ma, Li-Min, Zhong Wang, Hao Wang, Run-Sheng Li, Joan Zhou, Ben-Chun Liu, and Laurence S. Baskin. Estrogen Effects on Fetal Penile and Urethral Development in Organotypic Mouse Genital Tubercle Culture. Journal of Urology. 2009. 182. 2511-2517. DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2009.07.008 • Long, Susan E. Development and diagnosis of freemartinism in cattle. In Practice. Sept. 1990. 208210.