* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
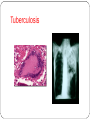
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
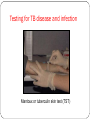
Microbiological safety for pathologists Dr David Mitchell Centre for infectious Diseases and Microbiology Westmead Hospital, Sydney Narrator: Dr Wendy Pryor Objectives Recognise most common infectious risks for pathologists List main routes of transmission List blood-borne viruses that pose laboratory risk Evaluate risks of infection after needlestick injury (NSI) Know what action to take following exposure Ensure you are properly screened and vaccinated Recognise potential risks of prions List general precautions to reduce risk Risks for pathologists by speciality Pathology speciality Biohazard Mode of transmission Clinical chemistry Blood-borne viruses Percutaneous exposure Haematology Blood-borne viruses Percutaneous exposure Histopathology Blood-borne viruses Percutaneous exposure TB Inhalation during autopsy/tissue processing Blood-borne viruses Percutaneous exposure TB, brucella, histoplasmosis, meningococcus Inhalation of culture Typhoid, shigella Contamination of hands Microbiology Autopsy-associated infections Risk recognised for centuries ~2% of total lab-associated infection Commonest cause of lab-acquired TB Newly recognised infections Potential routes of transmission during autopsies/tissue processing direct contact penetrating injury contamination of mucous membranes inhalation Infection risk in autopsies Pathogens may survive after death of the host, but rarely if ever multiply Risk should be lower from autopsy than invasive surgery on same individual if alive Mode(s) of transmission from a cadaver usually the same as from living host In some cases risk may be enhanced by autopsy (e.g. TB) or transmission may occur in unusual way If in doubt then apply the same infection control precautions as would apply during life Blood-borne viruses Occupational exposure to Hepatitis B Risk of transmission via NSI ~40% (if source HB(e )Ag +ve) ~5% (if source HB(e)Ab +ve) Management of HBV exposure (if not immune) HBIG within 72 hours of exposure commence vaccine course HBV vaccine 3 doses IM 0, 1 month, 6 months confirm post course immunity (anti-HB(s) antibody level) routine booster not needed usually give booster to healthcare workers after exposure Occupational exposure to HIV Risk of transmission of HIV via NSI ~0.3% via mucosal splash ~0.1% Management of occupational exposure baseline bloods and serology at 3 and 6 months if high risk, seek expert ID advice re antiviral prophylaxis (reduces transmission by ~80%?) during window period protect sexual partners, avoid pregnancy and blood donation. Occupational exposure to Hepatitis C Risk of transmission of HCV via NSI ~3.0% (1-10%) Management of occupational exposure to HCV baseline serology and HCV serology at 3 months HCV PCR at 6 weeks in high risk exposures monitor LFTs every 2 weeks no prophylaxis available early interferon treatment of acute Hepatitis C may reduce risk of chronic carriage and late complications Tuberculosis Tuberculosis Most important infectious risk in autopsies Relative risk for pathologists is ~10X that of non-clinical lab staff Airborne spread when infected body cavities are opened Possible percutaneous inoculation or splash Observers (e.g. medical students) and embalmers at risk Outbreaks in coroner’s offices, anatomy departments involving clerical staff etc Mycobacteria may remain viable despite formalin fixation Hospitals must have a TB monitoring programme Testing for TB disease and infection Mantoux or tuberculin skin test (TST) Screening policy: NSW Mortuary staff/pathologists - high risk TST at commencement of employment if positive - CXR and assessment if negative – repeat annually or after exposure if converts - CXR and medical assessment BCG – consider for high risk personnel, but not very efficacious Offer TST on termination All must be documented in employee’s file CJD and other prion diseases (1) Theoretical risk Pathologists do not appear to have greater risk of CJD than general population Prions not inactivated by formalin fixation or standard autoclaving High risk tissues brain, spinal cord, pituitary, dura mater, retina, optic nerve Lower risk tissues cornea, CSF, nerve ganglia, lymphoid tissue (eg tonsils, appendix), liver, lung, placenta, ?blood CJD and other prion diseases (2) Main theoretical risk of transmission during autopsy by percutaneous exposure to infected tissues or instruments IM injection of contaminated pituitary hormone Blood transfusion implicated in some human cases in UK CJD and other prion diseases (3) Australian Infection Control Guidelines for autopsies: Suspected cases should only be processed in appropriate facility Disposable personal protective equipment Disposable instruments Specific decontamination procedures Reducing infection risks – general principles Well designed facilities Written protocols and staff education Standard Precautions with all cadavers and specimens Appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) Minimise aerosols Hand hygiene Safe handling of sharps Decontamination of instruments and work surfaces Mandatory Hepatitis-B vaccination of staff Mandatory tuberculosis monitoring of staff Encourage staff to report exposure incidents Personal protective equipment - autopsies All staff, all autopsies regardless of infectious status surgical scrub, impervious gown, apron, overboots gloves (double surgical with interposed layer of mesh) N95 mask (surgical masks do not protect against infectious aerosols) face shield or eye goggles High risk autopsies: Consider PAPRs (powered air-purifying respirators) Standard N95 masks and respirator for high risk cases To protect yourself Always use Standard precautions Personal protective equipment Safe work practices with every case Always…… If there’s an incident Report it right away!