* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
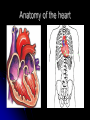
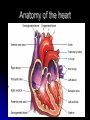
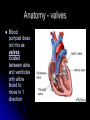
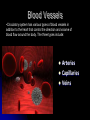
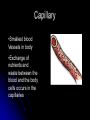
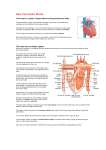
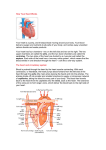
Circulatory System Chapter 6 – Page 186 Circulatory System contains: The heart Two closed circuits: - pulmonary circuit - systemic circuit Blood vessels Blood within our body What is the Heart? The heart is a hollow muscular structure made of up cardiac muscle Is about the size of a clenched fist It’s located in the centre of the chest, behind your sternum (slightly to the LHS). HEART = PUMP Functions of the Heart Circulate blood to all parts Transport water, oxygen, nutrients to cells Transport waste away from cells Helps maintain correct body temp (Homeostasis) Helps fight disease Anatomy of the heart Anatomy of the heart Anatomy There are 4 chambers to the heart, they consist of: Atrium's – The 2 upper chambers of the heart. 2 Ventricles – The 2 lower chambers of the heart. 2 Heart Anatomy Septum - Space that divides these chambers into two pumps The The Right Pump Left Pump Heart anatomy – 2 pumps Left pump = left atrium and left ventricle Pumps oxygen-rich blood for the body Red Right pump = right atrium and right ventricle Pumps carbon-dioxide-rich blood which goes to the lungs for removal of carbon dioxide Blue Circulation of the blood Worksheet -Pulmonary circulation - Systemic circulation Anatomy - valves Blood pumped does not mix as valves located between atria and ventricles only allow blood to move in 1 direction Blood Vessels •Circulatory system has various types of blood vessels in addition to the heart that control the direction and volume of blood flow around the body. The three types include: Arteries Capillaries Veins Arteries Carry oxygen-rich blood from heart to body Aorta largest artery in body HR = pressure of blood being pushed into arterial system Common points – carotid and radial pulse Veins •Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. •The deoxygenated blood has little oxygen and contains high amounts of waste products. Capillary •Smallest blood Vessels in body •Exchange of nutrients and waste between the blood and the body cells occurs in the capillaries Stroke Volume SV Blood pumped out of the left ventricle during each beat of the heart Average for an adult female may be about 60 millilitres per beat Whilst an endurance trained female could be up to 110 millilitres per beat Cardiac Output Q Amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute Measured in litres Q = HR x SV E.g. 70bpm x 80ml = 5.6L per Minute Cardiac output – continued At rest for the average male is around 5 -6 litres per minute This may rise to around 20 litres during exercise An endurance trained athlete could reach 30-35 litres per minute E.g. Lance Armstrong Blood Only body tissue that is liquid Blood cells make up 45% of the blood volume While plasma makes up the other 55% The three types of blood cell are: Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets BLOOD Blood carries the following to and from the body tissues: Heat Oxygen Vitamins Antibodies Hormones Waste materials Red Blood Cells: give blood its red colour Produced in the bone marrow Contains the protein haemoglobin 120 day life-span White Blood Cells: Fight infection Produced in the bone marrow 10 day life-span Platelets are cells that: Help form blood clots to stop bleeding Are produced in bone marrow Blood Pressure Systolic Pressure This is the upper reading and is the amount of pressure during the emptying stage of the heart Diastolic Pressure Is the lower reading and is the pressure on the arteries when the heart is relaxed Measures how hard the heart is working The health of the arteries, veins and capillaries