* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blood pressure
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
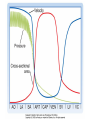
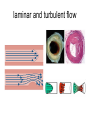
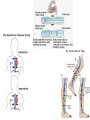
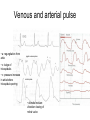
laminar and turbulent flow Distribution of blood circulation • Total volume of blood in all vessels (intravascular volume): – man: 5.4 l (77 ml / kg) – woman: 4.5 l (65 ml / kg) • Distribution: – Heart 7% – Pulmonary circulation 9% – Systemic circulation 84% • • • • from that veins 75% large arteries 15% small arteries 3% capilaries: 7% Pressure – flow – velocity – diameter - resistance Vessels branching TPR = 8..l/r4. if vessel of diameter 2 mm branches into two vessels than not to increase periferal resistance the diameter of each has to equals 1.68 mm (NOT for arterioles = resistance) Blood flow – depends on diameter power to 4, ie increase in diameter of 19% increases blood flow two times cardiac cycle Wiggers diagram A. B. C. D. E. F. G. atrial contraction, complete ventricular fillling, fourth sound due to turbulence ventr contraction, first sound due to valve closure, no ejection isovolumetric rapid ejection depolarization – reduced ejection second sound due to closure of aortic vlaves – isoV relaxation rapid ventricular filling, third sound due to turbulence reduced ventricular filling Venous system pressure -10 0 0 6 0 Sinus sagittalis 8 11 22 35 40 90 Pressures and volumes • Pulse (systolic) volume (PV)= 70 ml • Final diastolic volume (FDV)= 120 ml • Final systolic volume = 50 ml = functional reserve of heart • Normal systole ejects around 60% of FDV = Ejection fraction = PV/FDV. • Heart distribution = PV x frequency Venous and arterial pulse • a: regurgitation from atria jugular venous pulse • c: bulge of tricuspidalis • v: pressure increase in atria before tricuspidal opening carotic pulse • dicrotic incision: vibration closing of mitral valve