* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Reproductive System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
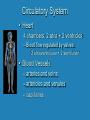
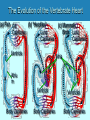
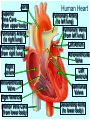
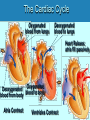
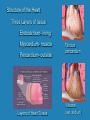
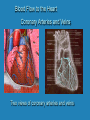
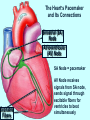
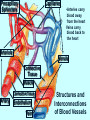
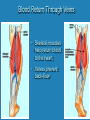
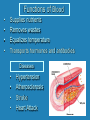
Heart Laboratory Circulatory System Organs and Cells Organization and Functions Circulatory System • Heart 4 chambers: 2 atria + 2 ventricles – Blood flow regulated by valves: 2 atrioventricular + 2 semilunar • Blood Vessels – arteries and veins – arterioles and venules – capillaries The Evolution of the Vertebrate Heart (a) Fish Gill (b) “Herptiles” Capillaries Lung Capillaries Ventricle (c) Mammals, Birds Lung Capillaries Atria Atriu m Ventricle Body Capillaries Body Capillaries Ventricles Body Capillaries Aorta Superior Vena Cava (from upper body) Pulmonary Artery (to right lung) Pulmonary Veins (from right lung) Right Atrium Atrioventricular Valve Right Ventricle Inferior Vena Cava (from lower body) Human Heart Pulmonary Artery (to left lung) Pulmonary Veins (from left lung) Left Atrium Atrioventricular Valve Left Ventricle Semilunar Valves Descending Aorta (to lower body) The Cardiac Cycle Oxygenated blood from lungs Deoxygenated blood to lungs Heart Relaxes; atria fill passively Oxygenated Deoxygenated blood from body blood to body Atria Contract Ventricles Contract Structure of the Heart Three Layers of tissue Endocardium- lining Myocardium- muscle Pericardium- outside Layers of Heart Tissue Fibrous pericardium Visceral pericardium The Structure of Cardiac Muscle Blood Flow to the Heart Coronary Arteries and Veins Two views of coronary arteries and veins The Heart’s Pacemaker and Its Connections Sinoatrial (SA) Node Atrioventricular (AV) Node SA Node = pacemaker Excitable Fibers AV Node receives signals from SA node, sends signal through excitable fibers for ventricles to beat simultaneously Heart Function Atrioventricular Valves Close “lubb” sound Semilunar Valves Close “dup” sound Atria Contract Ventricles Relax Atria Relax Ventricles Contract Heartbeat visualized with ECG Blood Pressure Blood pressure = Systolic pressure Diastolic pressure Systolic: pressure during ventricular contraction Diastolic: pressure during ventricular relaxation Precapillary Sphincters Capillaries •Arteries carry blood away from the heart Veins carry blood back to the heart Arteriole Venule Connective Tissue Muscle ConnectiveTissue Artery Endothelium Vein Structures and Interconnections of Blood Vessels Blood Return Through Veins • Skeletal muscles help return blood to the heart • Valves prevent back-flow Blood Components Plasma is the fluid portion of blood. Platelets initiate blood clotting Lipid Carriers distribute triglycerides and cholesterol. LDL = low density lipoprotein delivers cholesterol HDL= high density lipoprotein returns cholesterol to liver for destruction White blood cells defend against invaders Red blood cells carry oxygen Functions of Blood • • • • Supplies nutrients Removes wastes Equalizes temperature Transports hormones and antibodies Diseases • • • • Hypertension Atherosclerosis Stroke Heart Attack Worksheet • Complete pages 137-138 from lab manual • Be sure your instructor checks your completed worksheet before you leave the lab