* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECG Leads
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
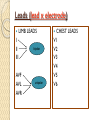
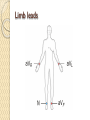
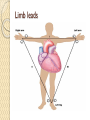
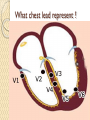
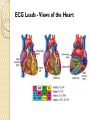
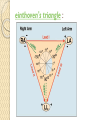
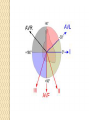
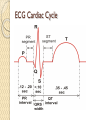
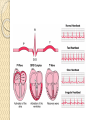
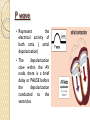
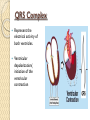
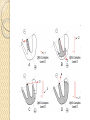
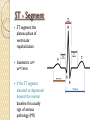
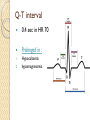
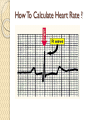
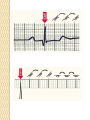
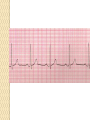
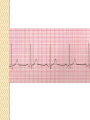
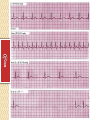
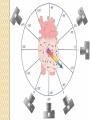
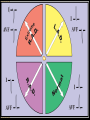
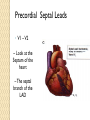
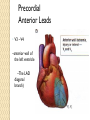
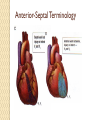
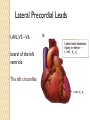
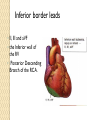
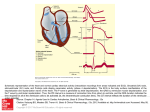
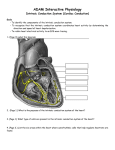
ECG Electrocardiography It is a voltage difference, record the electrical activity of the heart as well as valuable information about the heart function and structure. Willem Einthoven 1924 Leads (lead x electrode) LIMB LEADS I II III AVF AVL AVR bipolar unipolar CHEST LEADS V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 Limb leads Limb leads Both limb leads Chest leads What chest lead represent ? ECG Leads - Views of the Heart einthoven's triangle : ECG Paper ECG Speed 25mm/sec See video ECG Cardiac Cycle What is the isoelectric line؟ P wave Represent the electrical activity of both atria ( atrial depolarization) The depolarization slow within the AV node, there is a brief delay or PAUSE before the depolarization conducted to the ventricles Normal duration <0.12 sec Absent P wave: Atrial fibrillation SA Block AV Rhythm Peak P wave: Atrial hypertrophy PR interval Normally :0.12-0.2sec Prolonged in : heart block. Short in : W-P-W syndrome. QRS Complex Represent the electrical activity of both ventricles. Ventricular depolarization( initiation of the ventricular contraction QRS Complex Q wave R wave: S wave : :Normal QRS duration < 0.12 sec QRS Complex Q wave first downward deflection . septal depolarization. 0.04sec. R wave :first upward deflection. height: 5-8 mm. early ventricular depolarization S wave : late ventricular depolarization, Large QRS indicate Ventricular hypertrophy. ST - Segment ST segment: the plateau phase of ventricular repolarization. Isoelectric or> or<1mm. If the ST segment elevated or depressed beyond the normal baseline this usually sign of serious pathology. (MI) T- Wave T-wave :represent rapid phase of ventricular repolarization. peaked T wave: early MI hyperkalemia Black races Inverted : MI . Ventricular hypertrophy. Hypokalemia Digoxin Q-T interval 0.4 sec in HR 70 Prolonged in : 1. Hypocalcemia hypomagnesemia 2. U wave repolarization of the interventricular septum. low amplitude Prominent: suspect hypokalemia, hypercalcemia or hyperthyroidism J wave represents the approximate end of depolarization and the beginning of repolarization camel-hump sign Hypothermia hypocalcemia. . Low voltage ECG Obesity Emphysema COPD Severe hypothyroidism Rate Normal heart rate 60-100/ min < 60 called bradycardia >100 called tachycardia How To Calculate Heart Rate ? HR= HR= 300 No. of Large box btw R-R 1500 No. of Small box btw R-R RHYTHM Look For The Distance between Identical waves. Most commonly used R-R AXIS At any point during depolarization and repolarization electrical potential are being propagated in different directions. Most of these cancel each other out and only the net force is recorded. This net is called AXIS or cardiac VECTOR How To Check Axis in ECG Principles of ECG recording Explain the indication and the procedure for the patient. (assurance ) Ask the patient to take off any metals he/she wears. Expose the wanted sites. Cleaning of skin and shaving if necessary. Place the electrodes in the correct positions . Instruct the patient to remain still (should not talk during the test ) and relax their shoulders and legs while the recording takes place (1 min) See video How to comment on ECG Name.Age ,Date and time. Calibration and Speed of paper RAWIHI : RAWIHI R: rate, regularity,rhythm(sinus or asinus), A: axis. W:waves. I :intervals. H: hypertrophy. I: ischemia Normal Sinus Rhythm Rate = 60-100 beat / minute. The rhythm is regular All intervals are within normal limits There is a P for every QRS and a QRS for every P. P : QRS ratio = 1 : 1. The P waves all look the same Presence of P, QRS, T in each cycle. Normal shape, time of waves, segments and intervals Interfering factors Inaccurate placement of the electrodes Electrolyte imbalances Poor contact between the skin and the electrodes Movement or muscle twitching during the test Drugs that can affect results include digitalis, quinidine, and barbiturates MI When myocardial blood supply is abruptly reduced to a region of the heart, a sequence of injurious events occur : Ischemia ( subendocardial or transmural) Injury Necrosis, and eventual fibrosis (scarring) if the blood supply isn't restored in an appropriate period of time Hyperacute T wave is the earliest sign of acute myocardial infarction Precordial Septal Leads ◦ V1 – V2 – Look at the Septum of the heart – The septal branch of the LAD Precordial Anterior Leads ◦ V3 – V4 –anterior wall of the left ventricle –The LAD diagonal branch) Anterior-Septal Terminology Lateral Precordial Leads ◦ I,AVL,V5 – V6 ◦ lateral of the left ventricle ◦ The left circumflex Inferior border leads ◦ II, III and aVF ◦ the Inferior wall of the RV ◦ Posterior Descending Branch of the RCA. Posterior MI No leads look at the posterior wall. usually associated with inferior and/or lateral wall MI. The changes of posterior myocardial infarction are seen indirectly in the anterior precordial leads. Leads V1 to V3 face the endocardial surface of the posterior wall of the left ventricle. As these leads record from the opposite side of the heart instead of directly over the infarct, the changes of posterior infarction are reversed in these leads. The R waves increase in size, becoming broader and dominant, and are associated with ST depression and upright T waves. This contrasts with the Q waves, ST segment elevation, and T wave inversion seen in acute anterior myocardial infarction. ST depression is considered reciprocal ECG changes in what should be ST elevation for acute posterior wall injury. ECG Leads - Views of the Heart lead border V3 & V4 anterior Right RCA Ventricle Septum LAD V1 & V2 a VL,V5 & V6 II+III+AVF Arterial supply Lateral Left LCX Ventricle inferior RCA borderof right ventricle THANKS