* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
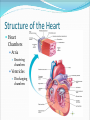
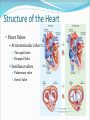
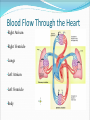
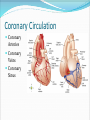
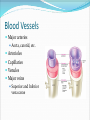
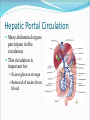
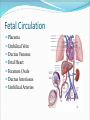
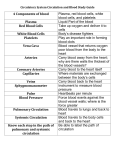
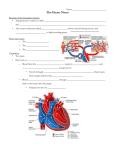
Dr. Tiffany N. Lee, BS, DC, FASA Seminar Outline Structure of the Heart Blood Flow Through the Heart Coronary circulation Conduction System of the Heart Blood vessels Hepatic Portal Circulation Fetal Circulation Blood Pressure Structure of the Heart Heart Chambers Atria Receiving chambers Ventricles Discharging chambers Structure of the Heart Heart Valves Atrioventricular valves Tricuspid valve Bicuspid Valve Semilunar valves Pulmonary valve Aortic Valve Structure of the Heart Heart Coverings Pericardium Parietal pericardium Visceral Pericardium, also known as the Epicardium Blood Flow Through the Heart •Right Atrium •Right Ventricle •Lungs •Left Atrium •Left Ventricle •Body Coronary Circulation Coronary Arteries Coronary Veins Coronary Sinus Case Study You hear that a friend has blocked coronary arteries. What are the possible causes? What could result if the condition is not treated? How can a coronary blockage be treated? Conduction System of the Heart SA (sinoatrial) node Also called the pacemaker AV (atrioventricular) node AV bundle (bundle of His) Purkinje fibers P-wave Depolarization of atria QRS complex Depolarization of ventricles T-wave Repolarization of ventricles Blood Vessels Major arteries Aorta, carotid, etc. Arterioles Capillaries Venules Major veins Superior and Inferior vena cavae Hepatic Portal Circulation Many abdominal organs participate in this circulation This circulation is important for: Excess glucose storage Removal of toxins from blood Fetal Circulation Placenta Umbilical Vein Ductus Venosus Fetal Heart Foramen Ovale Ductus Arteriosus Umbilical Arteries Factor Influencing Blood Pressure Blood volume Strength of heart contractions Heart rate Blood viscosity Resistance to blood flow Case Study Suppose an individual was injured in an automobile accident and his right arm was seriously damaged with copious blood loss. His blood pressure steadily dropped to dangerous levels. Explain how the loss of blood will reduce the blood pressure reading.