* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac Cath and Angiocardiography
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
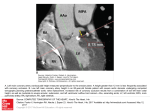
Cardiac Cath and Angiocardiography SPRING 2011 Catherization Studies and Procedures •Adults •Children Basic Diagnostic Studies of the Vascular System for Adults Cath of the LT side of the heart: ADULTS • Catheter introduced into the radial, brachial or femoral artery to the ascending aorta • Aortic root angio is performed to document competence of the aortic valve 4 Aorta Root Angiography • Normal means backward flow of the contrast media into the LT ventricle during injection • Atrial oximetry and blood pressure within aorta are measured • Then advanced into the LT ventricle 5 LT Ventriculography • Provides info on valvular competence • Interventricular septal integrity • Efficiency of the pumping action of LT ventricle • Pressure measurements are made • When systolic (LT ventricle) does not match systolic (aorta)- could mean aortic stenosis 6 Coronary Angiography • Allows the extent of intracoronary stenosis to be evaluated 7 Coronary Angiography 8 Coronary Angiography LT coronary artery Normal LT coronary Artery 9 Cath of the RT side of the heart: ADULTS 10 Cath of the RT side of the heart: ADULTS • Pressure measurements – Used to determine valvular heart disease – Congestive heart failure – Pulmonary hypertension – Cardiomyopathies 11 Exercise Hemodynamics • For evaluation of valvular disease – When fatigue and dyspnea are present • Simultaneous catherization is done and pressure measurements of RT & LT heart is taken – At rest – With exertion • Catheter is placed in: – An artery (femoral or brachial) – Vein (femoral or basilic) 12 Basic Diagnostic Studies of the Vascular System for Children • For evaluation of specific hemodynamic data – Selected aspects of cardiac function – Congenital heart defects • Methods are different according to age and size of the heart 13 Advanced Diagnostic Studies of the Vascular System for Adults & Children • Biopsy catheter with bioptome tip is inserted into jugular or femoral vein into RT ventricle • Jaws are opened and many biopsies are taken 14 Bioptome Biopsies • Used to monitor cardiac transplants for tissue rejection • And to differentiate between various types of cardiomyopathies 15 Studies of the Conduction System for Adults & Children Mulipolar catheters are inserted in •High RT atrium near sinus node •Atrioventricular apex •Coronary sinus 16 Studies of the Conduction System for Adults & Children • Sometimes 3 introducer sheaths are placed in one vein – Femoral – Internal jugular vein – Subclavian vein • Cathodes serve a dual function – Record electrical signals – Pace the heart 17 Interventional Procedures of the Vascular System: Adults • Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) – Also known as balloon angioplasty – Employs balloon to dilate the coronary artery stenosis • The placement of the catheter is placed much in the same way as standard coronary angiography 18 PTCA cont • Special steerable PTCA guidewire is used. • Guidewire is advanced to stenotic area through the balloon catheter • Balloon is pushed through to the stenotic area • Balloon is inflated and compresses fatty deposits 19 PTCA cont • Followed by arteriography to make sure it blood is flowing • This may be done repeated times to assure maximum dilatation • Restenosis occurs in 30-50% of patients 20 PTCA 21 PTCA with Stent placement • Similar to PTCA alone except a stent is placed • Restenosis is lower for pt’s who do this rather than conventional angioplasty alone 22 PTCA with Stenting 23 PTCA with Stent Placement 24 • Atherectomy devices remove the fatty deposit or thrombus material within artery Atherectomy • Directional coronary atherectomy devices having a specialized cutting device to shave out the plaque • There is a special nose cone that collect the free floating particles 25 Percutaneous transluminal coronary rotational atherectomy • The tip is a football shape and is embedded with diamond particles • Special torque guidewire between 160,000200,000 rpm • The plaque is pulverized into particles the size of RBC’s and removed by the reticuloendothial system 26 Interventional Procedures of the Vascular System: Children • Balloon Septostomy to enlarge a patent foramen ovale or preexisting atrial septal defect • This allows mixing of RT and LT blood – Resulting in improved arterial oxygenation • Balloon is passed through atrial septal opening into the LT atrium, inflated with contrast and pulled back through the orifice – Causes septum to tear 27 Balloon Septostomy with Transeptal System Approach • When there is not a preexisting hole in the atrial septum – Transeptal approach is used – Catheter with knife is employed into LT atrium blade is opened and pulled back through RT atrium – Then balloon septostomy may be performed to open the hole more 28 Interventional Procedures of the Conduction System: Adults & Children • Antiarrhythmic devices – Pacemakers – Implantable cardioverter defibrillators 29 CXR with Pacemaker 30 Post Catheterization Care • Firm pressure is applied to puncture site for 1530 minutes • Wound sites are cleaned and dressed • The patient will be observed in recovery for 4-8 hours • The insertion site will be checked frequently for signs of bleeding. • Medications and discharge instructions are given • Lots of fluid should be taken in • Vital signs should be monitored for 24 hours 31 Cardiac Catheterization Trends Trends • Vascular brachytherapy- technique where radiation is delivered to an area of a previously stented artery using endovascular techniques • Drug eluting stents- drug coated stents used for treatment of CAD to reduce restenosis 33 MRI • Is becoming more sophisticated and having greater detail and resolution • Allows for is to be used more often for the cardiovascular system • MRA is now able to assess anomalies in the coronary arteries – And identify calcifications in the coronary arteries and bypass grafts 34 Electron Beam CT • Can detect heart disease at it earliest and most treatable stages – Measures the amount of coronary calcium, • Electron Beam angiography is a simple and noninvasive technique that uses IV contrast media injection – Effective for visualization of great vessels, carotid arteries and peripheral vasculature 35