* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download circulation powerpoint
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
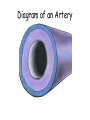
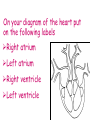
• Blood is a tissue that transports substances around the body • Blood carries oxygen and glucose to the cells of the body and transports waste and carbon dioxide away from the cells. • It contains red and white blood cells and platelets floating in liquid plasma. • Red blood cells contain a red pigment called haemoglobin that carries oxygen. Red blood cells are the part of blood that gives it it’s colour. They also have a large surface area and are without a nucleus to make more room for oxygen. • White blood cells fight pathogens to prevent disease. They do this by producing antibodies or carrying out phagocytosis. • Platelets are small fragments of cells that help the blood to clot by forming a network with proteins in the blood. • Plasma is a pale yellow liquid which contains nutrients such as glucose, waste products such as carbon dioxide and chemicals. All the blood cells float in the plasma. There are three types of blood vessels in our bodies: 1) Arteries 2) Veins 3) Capillaries Arteries carry blood away from the heart. The blood coming from the heart has to be pumped at high pressure around the body so arteries have thick, elastic walls to withstand the high pressure of the blood. As the blood is pumped, the walls flex and recoil, we can feel this if we put our fingers on our necks or wrists. It is called a pulse. Diagram of an Artery Veins carry blood to the heart. The blood going to the heart is at lower pressure than that in the arteries so veins have thinner walls and valves to stop the blood flowing back the wrong way. Diagram of a Vein Capillaries carry nutrients and oxygen to cells and remove carbon dioxide and waste from cells. Capillaries have walls that are just one cell thick to allow these substances to pass in and out of the blood easily. Diagram of a Capillary Blood is pumped from the heart through the arteries, these get smaller and smaller until they become capillaries which carry the nutrients and oxygen to the cells. The capillaries then join together again to form veins and carry waste and carbon dioxide back to the heart. • The heart is a pump • It is made of a special type of muscle called cardiac muscle • It pumps blood around your body • It is the size of your fist • It is divided in half to produce a left and a right side • Each side has two chambers • The upper chambers are called the ATRIA • They receive blood into the heart • The lower chambers are called the VENTRICLES • They pump blood out of the heart On your diagram of the heart put on the following labels Right atrium Left atrium Right ventricle Left ventricle Double Circulation • Blood passes through the heart twice on one journey around the body • It goes through the heart first to be sent to the lungs • It then returns to the heart • Second time it is pumped around the body • This is known as double circulation On your diagram of the heart put on the following labels From the lungs To the lungs From the body To the body Can you resuscitate this man??? • • • • • • www.skoool.co.uk On London Grid for Learning Key stage 3 Biology 37. The Circulatory System Coronary arteries become blocked with deposits of cholesterol This cuts off blood supply to the heart muscle The cells do not have oxygen or glucose Therefore they cannot respire No energy is produced Muscles cannot contract Heart stops beating Heart Attacks • The muscle cells will respire anaerobically for a short time. • This produces lactic acid and cramp • This is what causes the pain in a heart attack Risk Factors • High Cholesterol Diet • Stress • Smoking • Lack of Exercise • High Blood Pressure One of the problems about a heart attack is that the ventricles flutter irregularly rather than beating properly. In the 1970’s, Frank Pantridge, working at the Royal Victoria Hospital in Belfast, invented a portable defibrillator. This gives the heart a short, sharp electric shock which is enough to get it beating properly again. It is small and light and can be carried in an ambulance or kept in workplaces, ready for use should someone have a heart attack. defibrillator demonstration