* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular-System-Part
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
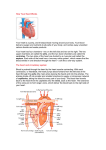
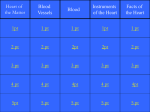
Cardiovascular System Part 2 Paths of Circulation • Pulmonary Circuit – Arteries carry blood from right ventricle to the – Alveolar capillaries in the lungs and • Alveolar capillaries exert less pressure than normal capillaries – Veins that lead back to the left atrium Paths of Circulation • Systemic Circuit – Left ventricle to all parts of the body (including the heart) – Vessels leading back to the heart – Includes aorta Arterial System • Ascending aorta – Contains right and left coronary arteries – Branches of the aortic arch: • Brachiocephalic • Left common corotid • Left subclavian arteries Venous System • Veins return blood back to the heart • Large veins parallel the paths of major arteries • The median cubital vein – Often used as site for venipuncture • The jugular vein drains: – Brain, neck, and head Venous System of the Abdominal Viscera • The blood in the hepatic portal system is rich in nutrients. • The blood from the abdominal viscera generally enters the hepatic portal system and is carried to the liver. • Liver helps regulate blood concentrations of glucose, amino acids, and lipids. Life-Span Changes • Plaque build-up may begin early • Heart rate and output decline slightly with age • Blood pressure increases with age, while resting heart rate decreases with age • Moderate exercise correlates to lower risk of heart disease in older people.