* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System The Heart
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
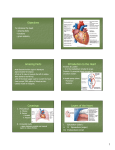
Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Cardi/o = ___ + vascul/ = ___ + -ar = ___ Abbreviation: CV = cardiovascular Structures of the CV system Major structures of the CV system are the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The Heart (first major structure of CV system) http://www.ohioheartandvascular.com/site/nucleus/si55551261.php Pericardium – double walled sac that surrounds the heart Peri = _____ + cardi = _____ + -ium = _____ Pericardial fluid between heart layers prevents friction during the heart beat. Three layers make up the walls of the heart: Epicardium – (epi = ____) outermost layer of the heart wall Myocardium – (myo = _____) middle layer of heart wall, thickest layer, contains heart muscle Endocardium – (endo = _____) innermost layer of the heart wall; See figure 5.3, p. 84 Facts: The coronary arteries & veins provide oxygen rich blood to the myocardium. If blood supply is disrupted, the myocardium in that area will die. Heart Chambers Atria – the two upper chambers of the heart. Receiving chambers for blood coming to the heart. Interatrial septum – separates the two atria from each other. Ventricles – the two lower chambers of the heart. All blood vessels leaving the heart begin in the ventricles. Interventricular septum – separates the two ventricles from each other Apex – lower tip of the heart http://www.bostonscientific.com/templatedata/imports/HTML/CRM/heart/hear t_chambers.html Heart Valves Valves are important to control the flow of blood from one chamber of the heart to another. Tricuspid valve – opening between right atria and right ventricle Pulmonary semilunar valve – opening between right ventricle and pulmonary artery Mitral valve (also called bicuspid) – opening between left atrium and left ventricle Aortic semilunar valve – located between left ventricle and aorta http://www.bostonscientific.com/templatedata/imports/HTML/CR M/heart/heart_valves.html Order of Blood Flow Superior and Inferior vena cavae Right Atrium Tricuspid valve Right Ventricle Pulmonary valve Pulmonary artery Lungs Pulmonary Veins Left Atrium Mitral Valve Left Ventricle Aortic valve Aorta to the body Superior and Inferior vena cavae Repeat the process Blood Flow Activity http://www.bostonscientific.com/templatedata/imports/HTML/C RM/heart/heart_bloodflow.html Cool Trivia: this is the only place where an artery will carry oxygen poor (deoxygenated) blood and a vein will carry oxygen rich (oxygenated) blood in the body.