* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrocardiography
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
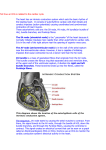
Electrocardiography A Brief Overview of ECG Interpretation Normal to Abnormal • Only way to understand abnormal is to first look at the “normal”. • First: looking at cardiac electrical conduction. Conduction System Sinoatrial Node Bundle of His Atrioventricular Node Bundle Branches Perkinje Fibres Conduction System • • • • • • Sinoatrial Node (60-80 bpm) Atrioventricular Node (40-60 bpm) Bundle of His (20-40 bpm) Bundle Branches Purkinje fibres Cardiac Cells Normal Conduction • SA node starts action • Accepted by AV node, starts inferior action • Passes to bundle of His, down Purkinje fibres • Action potential restarts Cardiac Cell Regular Muscle cells many more Nuclei per cell, whereas cardiac Muscle cells only have one. Much more like smooth muscle, Under involuntary control. Cardiac Cell Muscle Cell Conductivity • Contractile and Conductive cells • Focused impulse is generated (a pacemaker of any other site) then surrounding tissue will rhythmically contract. • Bad when not starting at node. Normal ECG Normal ECG Dysrhythmias • • • • Look at P Wave Look at QRS complex Look at T Wave Look for U Waves Rhythm Rate • In order to tell what the rate of the heart is from the ECG: • Count the # of QRS complexes in a six second strip and multiply by ten. Dysrhythmias • Rate • P Waves (present, inverted, absent, retrograde, ratio) • PR Interval (5 small squares) • QRS (3 small squares) • Rhythm (regular/irregular) Interpret me! Now me! Heart Disease • #1 killer in Canada Blocked Coronary Artery • depending on the amount of damage, conductive system may be impaired. • electrical impulses do not travel across dead tissue. Defibrillation • Reboot the computer Defibrillation • Definition - the application of an external electrical shock to the heart muscle which terminates the electrical activity of the heart. This allows the natural pacemakers of the heart to restore normal rhythm. • Time from collapse to defibrillation is critical factor to survival Ventricular Tachycardia Ventricular Fibrillation Non-Shockable Rhythms 12 Lead • Normally look at Lead II (over Left shoulder) • Sometimes need to look at more aspects of heart • Used to diagnose myocardial infarction, other cardiac dysrhythmias • Looks at 12 Different aspects of the heart 12 Lead Questions?