* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Conduction System of the Heart
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
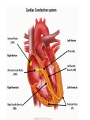
The Conduction System of the Heart The Conduction System • The heart is controlled by the autonomic nervous system(ANS) – it increases/decreases contraction, but it does NOT initiate it. • The heart has its own regulating system = conduction system • The conduction system is composed of specialized muscle tissue that generates action potentials within cardiac tissue. Components of the Conduction System 1. SA NODE • Located in the right atrial wall below the opening to the superior vena cava • Initiates heartbeat pacemaker • Average = 75 beats/minute 2. AV NODE • Located in the interatrial septum • Receives the action potential from the SA node • Action potential slows considerably allows time for the atria to empty into the ventricles Components of the Conduction System 3. AV BUNDLE • Receives impulse from the AV node • Located at the interventricular septum • Passes impulse onto the bundle branches 4. BUNDLE BRANCHES • Located below the AV bundle • Passes impulse onto the conduction myofibers 5. Purkinje Fibers • Located in the ventricular myocardium • Receives impulse from bundle branches and passes it onto ventricular myocardial cells to complete ventricle contractions. The Heart Beat The Heartbeat- usually heard by a stethoscope. The sound a ‘normal’ beating heart makes is ‘lub-dub’, this is known as a double beat. Problems can arise when the blood is not pumped properly. An ECG is used record electrical impulses sent by the heart. It measures: -Any damage to the heart -How fast your heart is beating and whether it is beating normally -The effects of drugs or devices used to control the heart (such as a pacemaker) -The size and position of your heart chambers The Cardiac Cycle Systole: the phase of contraction of a chamber (Systolic Number – This is the TOP number in your blood pressure…related to the pressure of contraction in the heart that is placed on the inside of the vessels) Diastole: the phase of relaxation (Diastolic Number – This is the BOTTOM number in your blood pressure…related to the relaxed phase of your heart that is then transferred to your vessels) Blood Pressure - Pressure exerted on the vessels as the blood is pumped through the heart. - Average blood pressure is 110-130/70-90 for average teenager. - Measure using BP cuff (sphygmomanometer) - Depends on 2 factors- cardiac output and the resistance in the arteries, which is related to their elasticity. - BP varies according to what factors? Cardiac Output • Cardiac Output: the amount of blood ejected from the left ventricle into the aorta OR the right ventricle into the pulmonary trunk per minute • It is determined by: 1. The amount of blood pumped by the left (or right) ventricle during each beat 2. The number of heart beats per minute • The amount of blood ejected by a ventricle during each contraction is called = ? Cardiac Output • • • • For an adult at rest… Stroke volume = ~70 mL (average) Heart rate = 75 beats per minute (average) Therefore, Cardiac Output (CO) = Stroke Volume x Beats per Minute CO = 70 mL x 75/min CO = 52.50 mL/min or 5.25 L/min