* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System Outline
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
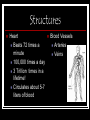
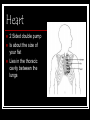
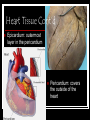
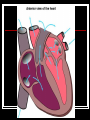
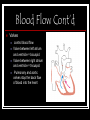
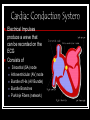
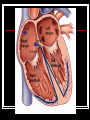
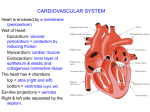
Cardiovascular System Outline Structures Heart Beats 72 times a minute 100,000 times a day 3 Trillion times in a lifetime! Circulates about 5-7 liters of blood Blood Vessels Arteries Veins Functions Transport nutrients and oxygen Transport waste to kidneys Distribute hormones and antibodies Help control body temperature and maintain homeostasis Heart 2 Sided double pump Is about the size of your fist Lies in the thoracic cavity between the lungs Heart Tissue Endocardium: smooth membranous lining inside the heart Myocardium: thickest layer, muscle tissue that is contractile. Heart Tissue Cont’d Epicardium: outermost layer in the pericardium Pericardium: covers the outside of the heart Parts of the Heart Divided into right and left sides 2 chambers in each side, for a total of 4 chambers Atrium: top, where blood enters Ventricles: bottom, where blood leaves Left and right sides separated by a partition called a septum Parts of the Heart Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle Right Ventricle Septum Heart Circulation Pulmonary: Flow of blood between the heart and lungs Systemic: Flow of blood between the heart and the cells of the body Coronary: Flow of blood within the heart Blood flow Review with heart anatomy Blood Flow Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Largest = Aorta Heart muscle contractions pump blood through arteries Veins carry blood towards the heart Largest = Superior/Inferior Vena Cava Valves prevent blood from returning to heart skeletal muscle contractions move blood through veins Blood Flow Cont’d Valves control blood flow Valve between left atrium and ventricle = bicuspid Valve between right atrium and ventricle = tricuspid Pulmonary and aortic valves stop the back flow of blood into the heart Review Blood flow: 4 square blood flow color sheet Cardiac Conduction System Electrical Impulses produce a wave that can be recorded on the ECG Consists of Sinoatrial (SA) node Atrioventriclular (AV) node Bundle of His (AV Bundle) Bundle Branches Purkinje Fibers (network) SA NODE Located in the upper right part of the atrium Is a natural pacemaker Fires at a rate of 60 to 100 times per minute The heartbeat starts in the SA node AV NODE Located in the floor of the right atrium Delays or slows the electrical impulse Fires at a rate of 40 to 60 time per minute Can take over if the SA node is not working Bundle of His Located next to the AV node Transfers the electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles Bundle Branches Located along the left and right side of the interventricular septum Act as pathways or a fork in the road Impulses in the bundle branch perform the important work of making the heart muscle contract Purkinje Network Provide an electrical pathway for each of the cardiac cells Activate the left and right ventricles simultaneously causing the ventricles to contract