* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart and Circulation
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
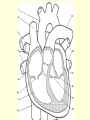
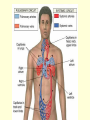
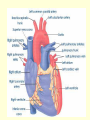
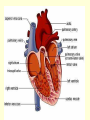
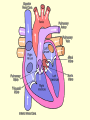
Diagram Word Bank • • • • • • • • Superior Vena Cava Inferior Vena Cava Right Ventricle Right Atrium Left Ventricle Aortic Arch Left Atrium Aorta • • • • Right Pulmonary Artery Left Pulmonary Artery Left Pulmonary Vein Aortic Semilunar (SL) Valve • Right Pulmonary Vein • Right Atrioventricular (AV)/Tricuspid Valve • Left Atrioventricular (AV)/Bicuspid/Mitral Valve Circulatory System Pre-Quiz 1. There are _____ liters of blood in the body. 2. The clear liquid that makes up 55% of the blood volume is ____________. 3. What cells are responsible for delivering oxygen and removing waste throughout the body? 4. The infection fighting cells found in blood are _______________. Circulatory System Pre-Quiz 5. What is the function of platelets in blood? 6. What element does hemoglobin contain? 7. ____________ carry blood away from the heart. 8. ____________ carry blood toward the heart. 9. A consistently high number of white blood cells is a symptom of __________, a cancer of the blood. Circulatory System Pre-Quiz 10. The average life cycle of a ____ ______ cell is 120 days, while ______ ________ cells have a shorter life cycle, living from a few days to a few weeks. What you will learn today . . . • • • • Atria are the receiving chambers for blood, while ventricles send the blood out of the heart Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while ventricles carry deoxygenated blood to the heart The aorta branches into smaller arteries that deliver oxygen to the organs and tissues The vena cavas branch into smaller veins that collect blood from organs and tissues and returns it to the heart The Heart and Circulation Introduction 1. The heart is the major organ of the circulatory system which includes the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Cardiovascular System Lymphatic System Introduction 2. The function of the heart is to pump blood through arteries, which connect to smaller arterioles, which connect to capillaries. 3. When blood is in the capillaries, it delivers oxygen to the tissues surrounding them and picks up carbon dioxide and other wastes from them. 4. The blood then returns to the heart via venules that are connected to bigger veins. Introduction 5. The heart is actually considered to be a double pump, as each side pumps blood to different parts of the body a. Pulmonary Circuit: the right side of the heart; sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs to pick up more oxygen b. Systemic Circuit: the left side of the heart; sends oxygenated blood to the body to be delivered to tissues and organs The Heart 1.Characteristics a. Size of a fist b. Hollow and cone-shaped c. Weighs less than a pound d. Tips to the left e. The bottom, called the apex, rests on the diaphragm (between the 5th and 6th ribs) The Heart 2. Atria ( singular = atrium) a. Receiving chambers for blood b. Push blood into the ventricles c. Small and thin-walled chambers d. Each atria has an auricle, which is a flaplike, wrinkled appendage e. Internal walls are made of muscle bundles called pectinate muscles The Heart 3. AV Valves (Atrioventricular valves) a. Each valve has tiny white collagen cords called chordae tendinae b. The cords anchor the flaps in closed position c. Consists of the TRICUSPID and BICUSPID (MITRAL) The Heart 4. Ventricles a. Propel blood for circulation to the entire body b. Very muscular walls, especially on the left – why? c. Inner walls have muscle folds called trabeculae carne. Some of the muscles are projections called papillary muscles that connect to the cords of the AV valves. The Heart 5. SL Valves (Semilunar valves) a. Connects the ventricles to the arteries b. Two types -Pulmonary -Aortic The Heart Song The Heart Song The right atrium’s where the process begins, when the CO2 blood enters the heart. And the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle, the pulmonary artery and lungs. Once inside the lungs it dumps its carbon dioxide and picks up its oxygen supply. And then it’s back to the heart through the pulmonary veins through the atrium and left ventricle. What happens to the blood AFTER it leaves the heart? • Blood Vessels Diagram • Animation • Review References • http://www.istockphoto.com/file_thumbview_approve/615 5504/2/istockphoto_6155504-cardiovascular-system.jpg • http://www.dkimages.com/discover/previews/880/450307 27.JPG • http://www.osovo.com/diagram/HumanHeartDiagram.JP G • http://www.raneyzusman.com/uploaded_files/Image/hum an_heart_diagram.gif • http://www.smm.org/heart/lessons/gifs/heartDiagram.gif • http://image.tutorvista.com/content/circulationanimals/mammalian-heart-external-view.jpeg • as.miami.edu