* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cardiovascular3
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
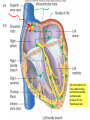
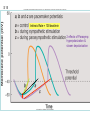
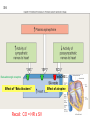
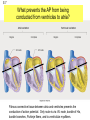
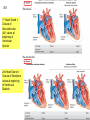
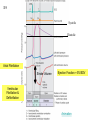
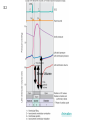
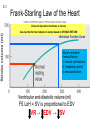
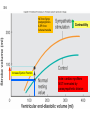
Abstracts and Test 2 • Earning up to 5 points for Test # 2 based on topics of Frog Heart Lab: – Regulation of pacemaker cells by temperature, hormones, neurotransmitters, antagonists – Heart block: 1st, 2nd, and 3rd degree – The conducting system – Strategies for prolonging survival of in vitro organs Cardiac Cycle Animation 1QQ #24 for 10:30 Write each letter and circle the letter of correct statements. a) Heart murmurs are caused by the closure of heart valves. b) The first heart sound is produced by the closure of the atrioventricular valves. c) Blood is about 65% plasma. d) Pacemaker cells produce action potentials that last about 200-300 milliseconds. e) Chordae tendonae and papillary muscles prevent eversion of the semilunar valves. 1QQ #24 for 11:30 Write each letter and circle the letter of correct statements. a) The buffy coat is thicker in a person with an infection. b) The first heart sound is produced by the closure of the atrioventricular valves. c) Blood is about 45% plasma. d) Pacemaker cells produce action potentials that last about 200-300 milliseconds. e) The tricuspid valve is situated between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. S8 F=Q=ΔP/R Flow = Pressure gradient/Resistance from Ohm’s Law (V=IR) 44 RR==8Lη/πr 8Lη/πr Q= ΔP πr4 8Lη Poiseulle’s equation Double radius … 16x flow Half radius….1/16th flow S1 Cardiac Output = Heart Rate X Stroke Volume What regulates heart rate? What regulates Stroke Volume? CO = HR x SV 5L/min = 72 beat/min x 70 ml/beat The Cardiac Cycle animation S4 Figure 12.11 S5 SA node cells do not have stable resting membrane potential, spontaneously produce AP, are Pacemaker cells S 15 Figure 12.22 Intrinsic Rate = 100 beat/min 2 effects of Parasymp: hyperpolarization & slower depolarization S6 NE Beta-adrenergic receptors Effect of “Beta blockers” Recall: CO = HR x SV EPI ACh mAChR Effect of atropine S7 What prevents the AP from being conducted from ventricles to atria? Fibrous connective tissue between atria and ventricles prevents the conduction of action potential. Only route is via AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, Purkinje fibers, and to ventriclular myofibers. S8 “Sis-toe-lee” 1st Heart Sound = Closure of Atrioventricular (AV) valves at beginning of Ventricular Systole “die-ass-toe-lee” 2nd Heart Sound = Closure of Semilunar valves at beginning of Ventricular Diastole S9 Figure 12.20 Systolic Diastolic Atrial Fibrillation Stroke Volume Ejection Fraction = SV/EDV Ventricular Fibrillation & Defibrillation Animation S 10 Events are same for Cardiac Cycle for Right Side of Heart; only difference is lower systolic pressures in right atrium and right ventricle. S1 So far, we’ve dealt with the factors that control Cardiac Output by changing heart rate. 3 CO = HR x SV 2 + sympathetic - parasympathetic 1 5L/min = 72 beat/min x 70 ml/beat 35L/min = ? beat/min x ? ml/beat The Cardiac Cycle animation S2 Figure 12.20 Stroke Volume Animation S3 Frank-Starling Law of the Heart Does not depend on hormones or nerves Assures that the heart adjusts its output based on VENOUS RETURN Ventricular Function Curve Ways to enhance Venous Return: 1) muscle contractions 2) “respiratory pump” 3) venoconstriction FS LoH = SV is proportional to EDV ↑VR→ ↑EDV → ↑SV Respiratory pump Mechanical pump for bedridden patients Muscle pump S4 Length-tension “curve” for Cardiac muscle Fig. 09.21 High EDV Low EDV Overinflation of ventricles leads to less effective pumping S5 Overinflation of ventricles results in reduction in stroke volume Treatments? …..diuretics S6 NE from Symp postganglionics & EPI from Adrenal medulla Contractility Increase Ejection Fraction Note: cardiac myofibers NOT innervated by parasympathetic division S7 3 Effects of Sympathetic Stimulation 1: Increase rate of contraction 2: Increase peak tension 3: Decrease twitch duration Why should the contraction be shorter? S8 Summary: Control of Stroke Volume FS LoH • End diastolic volume (preload) • Contractility (strength of ventricular contraction due to adrenergic stimulation) • Pressure in arteries that must be overcome = Afterload Afterload is analogous to trying to pump more air into a tire that is already fully inflated (heart contracting to overcome diastolic pressure.) S9 High blood pressure increases the workload of the heart….. Cardiac hypertrophy….increase chance of irregular conduction of AP through heart Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy S 11 Factors that control Cardiac Output by changing heart rate and stroke volume. Afterload (MAP) CO = HR x SV + sympathetic - parasympathetic VR and EDV (FSLoH) Contractility (catecholamines) 5L/min = 72 beat/min x 70 ml/beat 35L/min = ? beat/min x ? ml/beat