* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The history of cardiac diagnosis
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
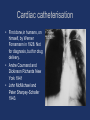
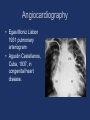
The Heart in Medicine Dr Caroline Coats Archivist, The British Cardiovascular Society [email protected] Cardiology: when did it start? • 1628 William Harvey De motu cordis • 1749 Jean Baptiste de Senac Traite de la structure du coeur • 1806 Jean Nicolas (Baron) Corvisart Essai sur les maladies du coeur • 1831 James Hope Diseases of the Heart • 1902 James Mackenzie Study of the pulse • The term Cardiology first used 1860 Cardiology Journals • National – 1908: Archives des Maladies du Coeur (France) – 1908: Zentralblatt fur Herzkrankheiten, (Germany) – 1909: Heart (UK) – British Heart Journal 1939 – Heart 1994 – 1916: Malatti du cuore (Italy) – 1925: American Heart Journal (USA) • Continental and Global – 1980: European Heart Journal – 1981: International Journal of Cardiology • Currently >100 print journals Cardiac Societies • 1922: The Cardiac Club (British Cardiac Society 1946). • 1924: The American Heart Association • 1927: Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Kreislaufforschung. – Belgian (1934), Italian (1935), French (1937) and Swiss (1948) Cardiac Societies were subsequently formed. • 1949: American College of Cardiology • Support for cardiac research came from cardiac societies and governments Milestones Diagnostics Therapeutics Physiology Anatomy Surgery The Pulse • 5th C BC Chinese physician Pein Ts Lo; pulse theory. Separate pulses connected to various organs eg liver and spleen • 3rd C BC Herophilus of Alexandria said that the pulse was created by “pneuma expressed from the heart” • Claudius Galen AD 131-201 wrote 18 books on the pulse Counting the pulse • !n 1583 Galileo Galilei invented the first device to measure the pulse rate, The Pulsilogium William Harvey 1628 “I am obliged to conclude that in animals the blood is driven round a circuit with an unceasing, circular sort of movement, that this is an activity or function of the heart which it carries out by virtue of its pulsation, and that in sum it constitutes the sole reason for the heart’s pulsatile movement” et Sanguinis in Animalibus Pathology of the Heart • Gioavanni Battista Morgagni 1682-1771 • De sedibus et Causus Morborum per Anatomen • 3 volumes 1761 • Described valve lesions and calcified coronary artery. • Completed at age 79. Invention of the stethoscope • De l’auscultation mediate ou traite du diagnostic des maladies des poumons et du coeur • 1819 René-Théophile-Hyacinthe Laënnec 1781-1836 Physiology….. methods of recording • Thomas Young invented the first rotating drum for recording in 1805 • J L M Poiseuille invented the mercury manometer in 1828. Dudgeons Sphygmograph 1876 Blood pressure measurement • The Reverend Stephen Hales 16771761 • The first to measure BP – in animals Diastolic blood pressure James Mackenzie Mackenzie’s clinical polygraph The first human electrocardiogram 1887 Augustus Waller The modern electrocardiogram • Willem Einthoven 1860-1927 Professor of physiology Leiden. Invented the string galvanometer in 1901. Thomas Lewis 1881-1945 • Welshman born in Cardiff. Student at UCL and Physician at UCH. Founded the Medical Research Society. Been and gone • Phonocardiography 1905 – 1965 – recording heart sounds and murmurs • Ballistocardiography 1920- 1960, recording cardiac pulsation • Vectorcardiography 1925-1950 – recording the ECG in 2 and 3 planes X-Rays • 1895 Wilhelm Roentgen – Discovery of X-Rays • 1896 EH Williams – Fluoroscopy – 1st case was a man with an enlarged heart – Difficult to image because it was moving Cardiac catheterisation • First done,in humans, on himself, by Werner Forssmann in 1928. Not for diagnosis, but for drug delivery. • Andre Cournand and Dickinson Richards New York 1941 • John McMichael and Peter Sharpey-Schafer 1943. Angiocardiography • Egas Moniz Lisbon 1931 pulmonary arteriogram • Agustin Castellanos, Cuba, 1937, in congenital heart disease. Coronary arteriography • First performed by Mason Sones at the Cleveland Clinic in 1962. – He did this by accident – It had been thought to be very dangerous Interventional cardiology 1929 Forsmann 1977 Gruentzig 2002 Cribier Catheterisation Angioplasty 1st TAVI 1962 Sones 1986 Puel and Sigwart 2003 Industry Coronary angiography 1st coronary stent Drug eluting stents ?dissolvable Ultrasound - to echocardiography • Based on the piezoelectric principle discovered in 1880 by Pierre Curie. • Ultrasound can be transmitted through many substances with echoes being reflected back at interfaces having different acoustic impedance. Cardiac surgery • 1820 Dominique (Baron) Larrey Pericardial effusion • 1893 TH Billroth “Any surgeon who would attempt an operation on the heart should lose the respect of his colleagues” • 1896 Guido Farino stab wound of right ventricle • 1925 Henry Souttar mitral valvotomy • 1938 Ductus • 1944 Coarctation • 1945 Blalock-Taussig shunt • 1947 Pulmonary valvotomy • 1948 Mitral valvotomy • Open heart surgery was needed especially for congenital lesions Open heart surgery • Hypothermia. – Cooling body to 30C allowed about 7 minutes circulatory arrest. – Devised in Toronto by W Bigelow in 1950 – Thomas Holmes Sellors closed 450 ASDs mortality 1.5% Open heart surgery • Cardio-pulmonary by pass (heart lung machine) – Started in USA 1953 by John Gibbon – then the Mayo Clinic with John Kirklin – Denis Melrose, London (also potassium arrest) • Cardiac transplantation 1967 – C Barnard. World wide moratorium – Cyclosporine 1980 for rejection • Off-pump bypass 1990 Heart Failure Heart Failure • • • • • • • • Definition c. AD 500 Egypt Sea Squill 1785 William Withering Foxglove (Digitalis purpurea) 1895 James Mackenzie atrial fibrillation 1920 Mercury (Mersalyl) chance discovery 1928 Lewis Special bed (dyspnoea and oedema) Fluid drainage; legs, chest. 1958 First modern diuretic chlorothiazide chance discovery via sulphonamide treatment • 1960 onwards; several new drugs Cardiac arrhythmias • • • • • • • • Digitalis 1914 Quinidine (discovered by a patient) 1961 Amiodarone (via a plant compound) 1950-1960 Pacemakers 1958 Transvenous pacing 1958 Implantable pacemaker 1950 onwards Electrical cardioversion 1980 Ablation of arrhythmias Pacemakers • 1932 Albert Hyman, engineer • 1958 1st pacemaker implanted • 1970 1st defibrillator implanted Coronary artery disease • • • • • 1772 William Heberden “Angina pectoris” 1867 Amyl nitrite Lauder Brunton then GTN 1912 Myocardial infarction identified J Herrick 1950 First use of electrical defibrillation 1960 CPR, W B Kouwenhoven • However cardiac massage was first used for cardiac arrest-during surgical operations - in 1901 by K Igelsrud in Tromso and 1902 Lane in London [via intact diaphragm] Modern era of coronary disease • • • • • 1960 Cardio-Pulmonary resuscitation 1961 Coronary care unit Desmond Julian 1962 Beta blocking drugs James Black 1970 Thrombolysis Aspirin Various procedures on coronary arteries – [a] coronary by pass surgery – [b] angioplasty & stents – [c] primary angioplasty for acute MI • 1985 Statins for lipid control