* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular Health - Riverside City College
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
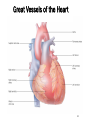
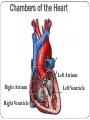
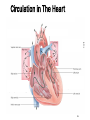
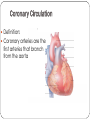
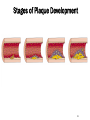
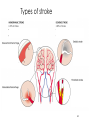
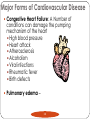
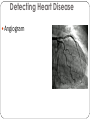
Cardiovascular Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Leading cause of death in the U.S. Affects nearly 81 million Americans Claims one life every 38 seconds The high rate of CVD is primarily caused by American’s lifestyles 2 Major Risk Factors That Can Be Changed Tobacco Use Number-one preventable cause of CVD in U.S. Smoking harms the CV System in many ways: Damages the lining of arteries Reduces HDL’s Raises triglycerides and LDL’s Nicotine increases blood pressure & HR CO displaces O2 Causes platelets to become sticky, leading to clotting Speeds the development of fatty deposits in the arteries 3 Major Risk Factors That Can Be Changed Diabetes Death from CVD is 2 to 3 times more likely in obese people than in lean people. Higher rates of other CVD risk factors: Hypertension Obesity Unhealthy blood lipid levels Damaged endothelial cells More vulnerable to atherosclerosis 4 Major Risk Factors That Can Be Changed Blood Pressure Normal adult: Hypertensive adult : Cholesterol Levels Total cholesterol (mg/dl): LDL: HDL: Level of Physical Activity Physical activity: Major Risk Factors That Can’t Be Changed Heredity Multiple genes contribute Having a first-degree relative with CAD Aging 70% of Heart Attack victims Over the age of 55 Being male Men have higher risk of heart attack Ethnicity African Americans have higher risk of hypertension; Hispanics have a greater risk of HBP and angina; Asians have lower rates of CVD 6 The Cardiovascular System Components of the Cardiovascular System Heart: Blood vessels: Arteries – Veins – Capillaries – Blood: The Cardiovascular System Each heartbeat has two phases: Systole = Diastole = Reporting BP: Anatomy of the Heart Great Vessels of the Heart From left to right (front view of heart): Superior and Inferior vena cava Returns blood from body to heart Aorta Delivers blood to entire body from heart Pulmonary trunk Delivers blood to the lungs from the heart Great Vessels of the Heart 12 Chambers of the Heart Left Atrium Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Ventricle Circulation in The Heart Chambers of the Heart Right Atrium Receives deoxygenated blood from entire body Blood passes to right ventricle via tricuspid valve Right ventricle Pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs Left Atrium Receives oxygenated blood from lungs Blood passes to left ventricle via bicuspid valve Left Ventricle Pumps oxygenated blood to the body Circulation in The Heart 16 Coronary Circulation Definition: Coronary arteries are the first arteries that branch from the aorta Cardiovascular Disease Major Forms of Cardiovascular Disease Atherosclerosis Coronary Artery (Heart) Disease (heart attack, angina) Arrhythmias and Sudden Cardiac Death Congestive Heart Failure Stroke Major Forms of Cardiovascular Disease Atherosclerosis – When coronary arteries become blocked with plaque buildup this results in Symptoms of Heart Attack include: If an artery in a limb becomes narrowed or blocked this results 20 Stages of Plaque Development 21 Major Forms of Cardiovascular Disease • Angina – Arteries are narrowed by disease but open enough to deliver blood under normal circumstances • During times of stress heart can not receive enough oxygen • Usually felt as • Arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death – Electrical conduction system is disrupted 22 Major Forms of Cardiovascular Disease Stroke –when cells of the brain are starved of oxygenated blood for more than a few minutes, they die. Types of Strokes Ischemic stroke – blockage in a blood vessel Thrombotic stroke Embolic stroke Hemorrhagic stroke – blood vessel ruptures in the brain Intracerebral hemorrhage Subarachnoid hemorrhage Aneurysm 23 Types of stroke 24 Detecting Stroke A quick way to recognize a stroke is to ask the person to do three things: 1. “Smile”. If her smile droops on one side, or if she is unable to move or open one side of her mouth… 2. “Hold your arms out”. If the person cannot move one arm or hold one arm still… 3. “Repeat a simple, short sentence”. If she has trouble speaking… 25 The Effects of a Stroke Can Include Paralysis (possible) Walking disability Speech impairment Memory loss Behavior changes The area of brain damage will determine which part of the body is affected Treating Stroke For Ischemic Stroke For Hemorrhagic Stroke Transient Ischemic Attack If a stroke is detected late Major Forms of Cardiovascular Disease Congestive Heart Failure: A Number of conditions can damage the pumping mechanism of the heart High blood pressure Heart attack Atherosclerosis Alcoholism Viral infections Rheumatic fever Birth defects Pulmonary edema – 28 Other Forms of Heart Disease Congenital Heart Disease Defect/malformation of heart/blood vessels that you are born with Ex. “A hole in the heart” Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enlarged heart Can cause arrhythmias Rheumatic Heart Disease Resulting from a sequence of untreated streptococcal throat infections Up to 3% of untreated strep. Infections lead to rheumatic fever Detecting and Treating Heart Disease Tests Used to Detect Heart Disease Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) Echocardiography Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 31 Detecting Heart Disease Angiogram Treating Heart Disease Balloon angioplasty Treating Heart Disease Coronary Bypass Surgery Protecting Yourself Against Cardiovascular Disease Exercise regularly Avoid tobacco Know and manage your blood pressure (monitored once every two years) Know and manage your cholesterol levels Develop effective ways to handle stress and anger 35