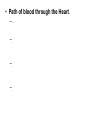* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System - Byron Senior High School
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
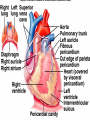
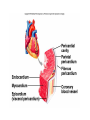
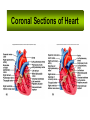
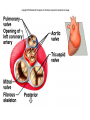
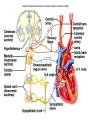
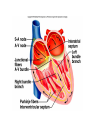
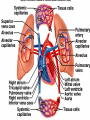
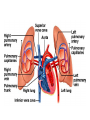
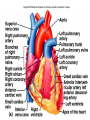
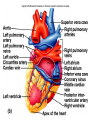
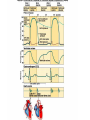
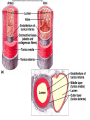
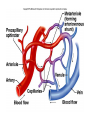
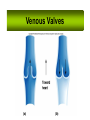
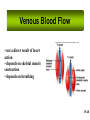
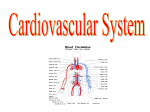
Cardiovascular System I. Introduction • The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, and vessels, arteries, capillaries, and veins. • A functional cardiovascular system is vital for _________________________and ___________from them. II. Structure of the Heart • The ______is a hollow, cone-shaped, muscular pump within the __________. • Size and Location of the Heart – The average adult heart is _______________wide. – The heart lies in the _______ under the sternum & ______________. Average Size of Heart • 14 cm long • 9 cm wide • Coverings of the Heart – The __________encloses the heart – It is made of ___________; the outer, tough connective tissue fibrous __________ surrounding a more delicate visceral pericardium (____________that surrounds the heart. – Between the 2 pericardia is a space (______________) filled with fluid • Wall of the Heart – The wall of the heart is composed of __________________ – The outermost layer, the ____________, is made up of connective tissue and houses ___________ and ________________. – The middle layer called ____________consists of ____________and is the thickest layer of the heart – The inner layer is the ______________. • Heart Chambers and Valves – The heart has four internal chambers: ____________on the top and ____________ on the bottom. • _______________returning to the heart from other parts of the body and have thin walls and ear-like auricles projecting from their exterior. • The thick-muscled _________________________ Coronal Sections of Heart – A __________ divides the atrium and ventricle on each side. Each also has an _____________________to ensure one way flow of blood. • ________________________ • ________________________ – Both have cusps to which __________________(heart strings) attach. • ______________are, in turn, attached to _______________in the inner heart wall that contract (pull) during ventricular contraction to ______________________through the A-V valves. – The _______________________bring deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium. – The __________________than does the left ventricle because it pumps blood only as far as the lungs, compared to the ____________________________________ ____________________________________ – At the base of the ______________leading to the lungs, is the ______________, which ____________________________________ ____________________________________ – The __________________receives blood from five pulmonary veins. – The _____________pumps blood into the entire body through the _______, guarded by the aortic valve that prevents backflow of blood into the ventricle. • Path of blood through the Heart. –. –. –. –. –. –. –. • Blood supply to the Heart Muscle – __________________ • Feed the heart muscle with oxygenated blood. – __________________ • Drain the blood from the heart muscle and carry it to the right atrium III. Heart Actions • Blood pressure is the force of blood against the inner walls of the arteries. • The cardiac cycle consists of: – Atria beating in unison (___________) – Contraction of both ventricles __________________________________________ _________________________________________ – Then the entire heart relaxes for a breif moment (________________________________) • ________ = ventricle contraction felt in the arteries • Heart sounds – ___________are due to the vibrations in heart tissue as blood rapidly changes velocity within the heart. – Heart sounds can be described as a “lubbdupp” sound, also called “___________” sounds – The “_____” occurs as ventricles contract – The “_____” occurs as ventricles relax IV. Blood Vessels • The blood vessels form a closed tube that carries blood away from the heart, to the cells, and back again to the heart. • _______ are thick vessels adapted for carrying high presure blood _____ from the heart • ________are the smallest vessels, through which substances are exchanged with cells • _______ are thinner than arteries; they _____ blood to the heart. Venous Valves Venous Blood Flow • not a direct result of heart action • depends on skeletal muscle contraction • depends on breathing 15-48 Life-Span Changes • deposition of cholesterol in blood vessels • heart enlarges • cardiac muscle cells die • fibrous connective tissue of heart increases • adipose tissue of heart increases • blood pressure increases • resting heart rate decreases 15-70 Clinical Application Arrhythmias Ventricular fibrillation • rapid, uncoordinated depolarization of ventricles Tachycardia • rapid heartbeat Atrial flutter • rapid rate of atrial depolarization 15-71