* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
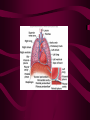
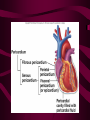
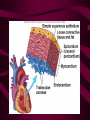
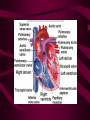
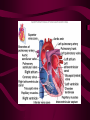
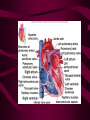
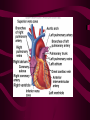
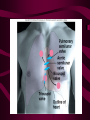
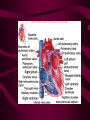
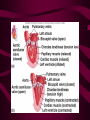
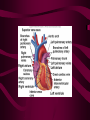
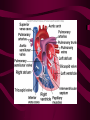
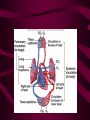
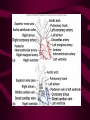
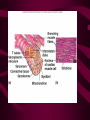
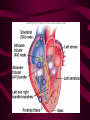
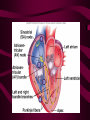
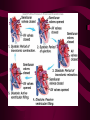
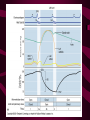
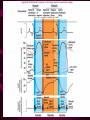
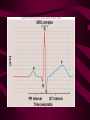
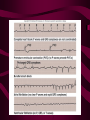
Cardiovascular System Heart Heart • • • • • Location – Mediastinum Pericardial Sac Pericardial Cavity Pericardial Fluid Parietal Pericardium Heart Wall • Epicardium = Visceral Pericardium • Myocardium – Trabeculae carneae • Endocardium Heart Chambers • Atria (Atrium) • Auricles • Interatrial septum Heart Chambers • Ventricles • Interventricular septum • Coronary sulcus Valves • Atrioventricular (Tricuspid & Bicuspid) – Chordae tendineae – Papillary muscles • Semilunar – Pulmonary – Aortic Vessels • • • • • Superior Vena Cava Inferior Vena Cava Pulmonary Trunk (Arteries) Pulmonary Veins Aorta Coronary Circulation • • • • • • Aorta Coronary arteries Myocardium Cardiac veins Coronary sinus Right atrium Cardiac Muscle physiology • • • • • Myocardium Automated excitement No graded responses No tetany No anaerobic metabolism Cardiac Muscle • • • • Striated, Involuntary Intercalated discs Refractory period prevents tetany Energy – ATP – aerobic metabolism – Coronary circulation providing O2 Excitation of cardiac muscle • Depolarization to threshold is spontaneous due to decreased outflow of K+ • Sinoatrial node (SA) – Depolarizes every .8 sec. At rest – Depolarizes due to change in permeability – Pacemaker Conduction • • • • • Spread to both atria AV node (.1 sec. Delay) AV Bundle (Bundle of His) Purkinje = Conduction fibers Myocardial cells of ventricle Cardiac Cycle • Systole • RV = 30 mm Hg • LV = 120 mm Hg Cardiac Cycle • Diastole Time for cardiac cycle • • • • • Entire cycle is .8 sec. Atrial systole .1 sec Atrial diastole .7 sec Ventricular systole .3 sec Ventricular diastole .5 sec Pressure Curves • Atrium • Ventricle • Aortic Heart Sounds • S1 = AV valves closing • S2 = Semilunar valves closing CARDIAC OUTPUT • CO = HR x SV • 5-6 liters/minute • 70 beats/minute x 80 mls/beat Cardiac Reserve • Difference between maximum CO and resting CO • Can increase 700%!! Heart Rate Control • Sympathetic Stimulation • Parasympathetic Stimulation Stroke Volume Control • SV = End-diastolic volume – End-systolic volume • End-diastolic volume – Length of diastole – Venous Return Stroke Volume Control • End-systolic volume – Frank-Starling Law – Sympathetic Nervous System – Parasympathetic Nervous System Factors influencing Cardiac Function • • • • • Cardiac Center in Brainstem Exercise,Temperature Ions (K, Ca, Na) Sex Age Electrocardiogram • • • • • EKG, ECG Leads P wave – atrial depolarization QRS complex – ventricular depolarization T wave - ventricular repolarization