* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Outline - University Health
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
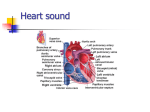
A Technique for Cardiac Auscultation Chapter 6 Ara G. Tilkian, MD, FACC Instructor Patricia L. Thomas, MBA, RCIS Outline • • • • • • • • • How to Proceed Patient Position Inspection and Palpation Palpating Thrills Inching Respiration Cardiac Auscultation of the Bony Chest Evaluation of Heart Sounds Summarized Evaluation of Heart Murmurs Summarized How to Proceed • Quiet room • Block out all other visual & auditory perceptions • Closing your eyes may help • Concentrating on one cardiac event at a time Patient Position • Recumbent, comfortable & relaxed • Examination from patient’s right side • Murmurs & gallop rhythms are louder in the recumbent position • In this position venous return to the heart is increased & can be further augmented by raising the patient’s legs • Patient’s left side mitral murmurs & thrills are best heard because the apex is closer to the chest wall • Sitting or standing sounds & pulsations may disappears Inspection & Palpation • PMI- point of maximal impulse • Rate of Rise: The Carotid Pulse-peak of pulsation – A normal ROR feels like a sharp tap – Abnormal ROR like a nudge or a weak tap • Pulsus Alternans – Regular rhythm with alternating strong and weak ventricular contractions – Alternation of S2 • Brachioradial Delay & Apical-Carotid Delay – Indicates aortic stenosis – Brach: Right Brachial and Right Radial artery – Apical: PMI & Right Carotid Artery Palpating Thrills • Palpable murmurs-low-pitched vibrations associated with heart murmurs • Best felt with palms of the hand • The thrill of AS radiates toward the right neck • The thrill of PS radiates toward the left neck • Look for jerking carotids & for venous pulsations “Inching” • Listen to first heart sound (intensity, variability, localization • Listen to second heart sound (It is split?) • Does it vary with respiration? Is P2 loud? • Listen for a third heart sound • Listen for any abnormal sounds such as S4 or a click • Listen for systolic murmurs then for diastolic murmurs Respiration • Inspiration causes right-sided cardiac events to be louder and delays left-sided events by a few seconds because of – – – – – – – – Decreased intrapleural pressure Increased venous return to the right heart Prolongation of RV systole Delay in PV closure Increase in pulmonary capacity Delay in venous return to the LA Shortening of LV systole Early closure of the AV Respiration cont… • In normal individuals: – The two components of S2 can usually be identified at the end of deep inspiration – S2 becomes one sound during expiration Evaluation of Heart Sounds Summarized • Are both S1 and S2 present? • Is each normal? • If not, is S1 loud, weak, or absent? Can both components of S1 be recognized? • Is S2 loud, weak, or absent? Is there normal splitting of S2 on inspiration? Is the splitting of S2 reversed (widest on expiration)? • Are there more than two heart sounds? Is the extra sound systole or diastolic? Is it closer to S1 or S2 and at what interval? What is its quality? Does it vary with respiration? • Is there a murmur? THE END OF CHAPTER 6 Tilkian, Ara MD Understanding Heart Sounds and Murmurs, Fourth Edition, W.B. Sunders Company. 2002, pp. 49-57.