* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nursing 259 - University of Hawaii
Survey
Document related concepts
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
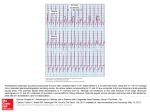
Basic EKG Interpretation Atrial Arrhythmias Atrial Arrhythmias Premature Atrial Contractions Atrial Tachycardia Paroxysmal NonParoxysmal Atrial Flutter Atrial Fibrillation Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC) Caused by enhanced automaticity Occurs in addition to underlying rhythm P wave of PAC Occurs early Different looking May have different PR interval QRS of PAC May be blocked or nonconducted – ventricle is still refractory Can be normal or wide in duration Effects of PAC May cause palpitations May be precursor to worse arrhythmias – such as atrial flutter or fibrillation May decrease cardiac output – occurs soon after previous beat, not enough time for ventricle to fill up again Premature Atrial Contraction (5th beat) Premature Atrial Contraction (5th beat) Blocked PAC Enlarged Photo PAC’s Common causes Emotions Caffeine Sympathomimetic drugs ischemia Treatment of PAC Usually none Eliminate cause PAC: Nursing Implications Monitor serum potassium levels Monitor serum digoxin levels Monitor for CHF Eliminate causes Monitor for more arrhythmias Atrial Tachycardia Rapid Atrial Arrhythmia Paroxysmal: Starts and stops suddenly Usually caused by reentry Usually initiated by PAC Nonparoxysmal: Sustained Usually caused by enhanced automaticity Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): Generic term when P waves can’t be seen Atrial Tachycardia P wave: Regular and upright, may be buried in preceding T wave; may be initiated by PAC Rate: 160 - 220 beats/minute Rhythm: Regular QRS: May be less than P waves because of block; may be normal or wide in duration Causes of Atrial Tachycardia Stress Excessive use of stimulants Accessory conduction pathway Chronic lung disease Digoxin toxicity (particularly atrial tach with block) Effects of Atrial Tachycardia May decrease cardiac output – tachycardia causes less time in diastole Decreased coronary perfusion coronary arteries get less blow flow as less time in diastole Chest pain – due to decreased coronary perfusion Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Tach with Block Non-Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia PAT Treatment of Atrial Tachycardia Vagal stimulation Carotid sinus massage Valsalva maneuver Diving reflex Synchronized cardioversion Overdrive pacing Adenosine IV: 6 mg rapidly, may give 12 mg in 1 -2 minutes Treatment of Atrial Tachycardia Diltiazem: 0.25 mg/kg bolus; then 10 mg/hr Digoxin IV except if arrhythmia is due to accessory conduction pathway or digoxin toxicity Amiodarone Beta-blockers Atenolol, metoprolol, esmolol Nursing Implications - Atrial Tachycardia Check for clues as to cause Monitor digoxin level Have resuscitative equipment available Supplemental oxygen Assess for chest pain and CHF Atrial Flutter Usually a transient rhythm Usually precedes atrial fibrillation Results either from reentry or enhanced automaticity Seen in people with ischemic heart or valvular disease Atrial Flutter Flutter waves: sawtooth pattern Atrial rate: 250-350 beats/minute Atrial rhythm: regular, may be buried in QRS complex PR interval: not measurable QRS: may appear distorted QRS rate: described in terms of ratio of F waves to QRS (4:1, 2:1) QRS rhythm: may be regular or irregular Atrial Flutter Atrial Flutter Atrial Flutter Atrial Flutter Effects Loss of Atrial Kick (delay of the impulse at the AV node so that the atria can contract to increase ventricular filling and cardiac output) Decreased cardiac output Treatments Amiodarone, procainamide, beta-blockers, digoxin, calcium channel blockers Cardioversion very effective Ibutilide (Corvert) - chemical cardioverter: 1 mg/50 D5W over 10 min; may repeat in 10 min Nursing Implications: Atrial Flutter Ensure adequate oxygenation For cardioversion: need informed consent, if elective, sedation and resuscitative equipment Atrial Fibrillation Due to enhanced automaticity Usually chronic rhythm Associated with: Ischemic heart disease Valvular disease Chronic lung disease Post cardiac surgery Hypokalemia Atrial Fibrillation Fibrillatory waves: wavy baseline Atrial rate: over 350 beats/minute Atrial rhythm: irregular PR interval: not measurable QRS: usually normal and alike QRS rate: may vary controlled: less than 100 beats/minute uncontrolled: over 100 beats/minute QRS rhythm: irregularly irregular Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation Effects: Loss of atrial kick May cause mural thrombi – thrombi on endocardial wall due to stagnant blood flow Treatment: Same as for atrial flutter Anticoagulate if over 48 hours duration Goal for chronic arrhythmia is to control ventricular rate Cardioversion less effective, if chronic – usually delayed if greater than 48 hours duration until anticoagulated and atrial thrombi excluded Atrial Fibrillation: Nursing Implications Consider this arrhythmia in irregular pulse with pulse deficit Monitor for CHF High risk for CVA Consider hyperthyroidism, alcoholic cardiomyopathy – may cause atrial fibrillation Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Due to several atrial and AV ectopic sites Associated with: Rheumatic heart disease Vagal stimulation Digoxin toxicity Usually no effects on client Wandering Atrial Pacemaker P waves: At least three different looking P waves. Some may be inverted PR interval varies QRS: Usually normal and alike Rate usually 60 - 100 beats/minute Rhythm usually irregular In rates greater than 100: Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) Wandering Atrial Pacemaker MAT Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Treatment: Usually none except if digoxin toxicity Coughing may help if due to vagal stimulation Treatment usually ineffective for MAT Nursing Implications: Monitor serum digoxin levels Monitor for bradycardia Monitor for hypotension