* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kickin’ Cardiovascular System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
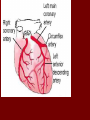
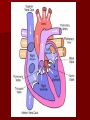
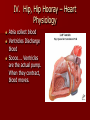
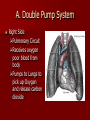
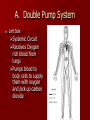
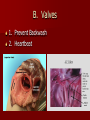
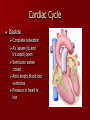
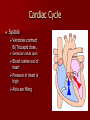
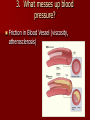
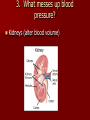
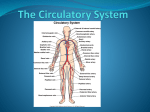
Crackin’ Cardiovascular System The Happy Heart Size of your fist Less than 1 pound Covered by pericardium Coronary arteries (blood vessels) – give heart blood 4 chambers – 2 atria (atrium) – receive blood, top of heart – 2 ventricles – discharge blood, bottom of heart Path of Blood Through the Heart 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Inferior/Superior Vena Cava (bring blood from body to heart) Right Atrium Tricuspid Valve Right Ventricle Pulmonary Semilunar Valve Pulmonary arteries Lungs – Release CO2 and picks up O2 Path of Blood Through the Heart 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Pulmonary Veins Left Atrium Bicuspid Valve Left Ventricle (biggest part) Aortic Semilunar Valve Aorta Arteries Capillaries (release O2 to cells, pick up CO2) Veins – Back to Heart AGAIN IV. Hip, Hip Hooray – Heart Physiology Atria collect blood Ventricles Discharge blood Soooo…. Ventricles are the actual pump. When they contract, blood moves. A. Double Pump System Right Side Pulmonary Circuit Receives oxygen poor blood from body Pumps to Lungs to pick up Oxygen and release carbon dioxide A. Double Pump System Left Side Systemic Circuit Receives Oxygen rich blood from lungs Pumps blood to body cells to supply them with oxygen and pick up carbon dioxide B. Valves 1. Prevent Backwash 2. Heartbeat B. Valves (cont) “lub”-AV valve closing; longer and louder sound “dub”-Semilunars closing; shorter and sharper Cardiac Cycle Diastole Complete relaxation AV valves (bi and tricuspid) open Semilunar valves closed Atria empty blood into ventricles Pressure in heart is low Cardiac Cycle Systole Ventricles contract Bi/Tricuspid close, Semilunar valves open Blood rushes out of heart Pressure in heart is high Atria are filling Arteries Take blood away from the heart No Valves High Pressure C. Veins Take blood toward the heart Valves to prevent backflow because... Low pressure, Thin Walls, Far from the heart and change in pressure D. Capillaries Connect arteries to veins Very thin Transparent, one-cell layer thick GAS EXCHANGE TAKES PLACE HERE Flow of blood through vessels Aorta Capillary Vein Heart E. Blood Vessel Physiology Arterial Pulse Pressure wave created by the expansion and recoil of an artery that occurs with each beat of the left ventricle. Average is 70-76 beats per minute Pulse points are listed in book. Take a look and try to find them on your body. 2. Blood Pressure Pressure the blood exerts against the inner walls of blood vessels. Force that keeps blood circulating between beats Pressure in arteries near the heart Systolic: Pressure in arteries at peak of ventricular contraction Diastolic: Pressure when ventricles are relaxing Procedure for taking blood pressure 1. 2. 3. 4. Pump up to about 150 (exceed systolic). Stops blood flow. Reduce pressure in cuff while listening carefully. When first soft tapping sounds are heard, SYSTOLIC As pressure is reduced, sounds get louder. When no sounds, record DIASTOLIC 3. What messes up blood pressure? Friction in Blood Vessel (viscosity, atherosclerosis) 3. What messes up blood pressure? Nervous System (narrows vessels)-fear, exercise, blood loss 3. What messes up blood pressure? Kidneys (alter blood volume) 3. What messes up blood pressure? Temperature (cold restricts vessels, hot dilates vessels) 3. What messes up blood pressure? Chemicals (alcohol & histamines dilate, nicotine constricts)