* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download files/uploads/Courses/Biology 5610/EKG
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
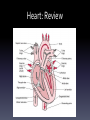
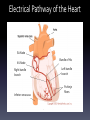
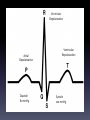
Human EKG Heart: Review Electrical Pathway of the Heart SA Node AV Node Right bundle branch Inferior vena cava Bundle of His Left bundle branch Purkinje fibers • Electrocardiogram EKG or ECG • Willem Einthoven-1903 • A record of the overall spread of electrical activity of the heart. • What EKG actually records: 1) NOT a direct recording of electrical activity. Recording a portion of electrical activity induced in body fluids by cardiac impulse that reaches the surface of the body. 2) NOT a recording of a single AP in a single cell at a single point in time. Represents the SUM of electrical activity in all of cardiac muscle cells. 3) Represents comparisons in voltage detected by electrodes at two different points on the body’s surface. Not actual potential. Einthoven’s Triangle • Determines the electrical axis of the heart. • Equilateral triangle. The vertices are at the left and right shoulders and the pubic region. • The center corresponds to the vector sum of all electric activity occurring in the heart at any given moment. • Based on 3 lead system. Now have 12 lead systems that are much more accurate. • Einthoven’s law: At any instant the potential of any wave in lead II is equal to the sum of potentials in leads I and III. Ventricular Depolarization Atrial Depolarization Diastole 80 mmHg Ventricular Repolarization Systole 120 mmHg Why is atrial repolarization not represented on the figure? Why Use EKG? • Detect Arrhythmias – Irregular heart beat • May indicate medical disorder or be due to physiological state. – Bradycardia = decrease heart rate (sinus node problem OR athlete) – Tachycardia = increase heart rate (imbalance of electrolytes OR exercise) Group Mean HB (BPM) Resting Adult 60-100 Adult male 70 Adult female 75 Teenager 80-100 Child 90-110 Toddler 100-130 Infant 130-150 Athlete 50-60 (lowest ever 25) Sleep 40 Exercise 220 Lance Armstrong 32-34 (resting) 201 (exercising) Elephant 28 Shrew > 800 Today’s Lab • EKG and Heart sounds. • Only do lab on 2 group members. • Only have to do resting EKG once for each member (ignore Experiment 1 in heart sounds lab). Homework!!!! • Answer all labscribe questions. • Write a results and methods section for this lab. Please attach a data sheet with all of your RAW data. • RAW data should not be a part of your results section! Results Section • Should concisely present your data. This section should have figures and/or tables AS WELL AS a paragraph explaining those data. • Don’t interpret the data, however, you should point out any trends (i.e. heart rate increases with increased activity or average heart rate was lower in males than females).