* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
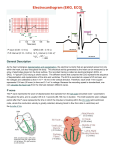
Download V. Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
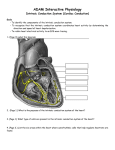
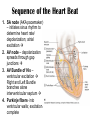
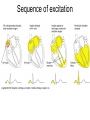
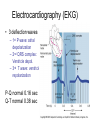
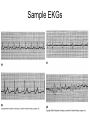
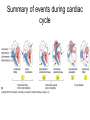
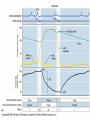
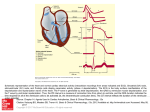
Heart Contraction Overview V. Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)- record impulses by detecting electrical currents in heart; measures voltage (mV), not contractions. Impulses lead to contractions. 1. Unique characteristics of cardiac muscle: 1.Stimulation- autorhythmicicity; depolarize spontaneously 2.Organ contraction- heart cells function as a unit as ions pass through gap junctions 3.Absolute refractory period- inexcitable period 2. Events of Contraction: 1.Sodium ions rush into cells creating action potential from –90 mV to +30 mV depolarization. 2.Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) release calcium. 3.Sarcomere contracts by sliding filaments of actin and myosin. 4.Calcium channels close + potassium enters the cells + sodium leaves = repolarization 5.resting potential back at –90 mV. Sequence of Excitation: (takes .22 sec) Sequence of the Heart Beat 1. SA node (AKA pacemaker) – initiates sinus rhythm to determine heart rate/ depolarization; atrial excitation 2. AV node – depolarization spreads through gap junctions 3. AV Bundle of His – ventricular excitation Right and Left Bundle branches alone interventricular septum 4. Purkinje fibers- into ventricular walls; excitation complete Sequence of excitation Mechanism and events of a contraction Sequence of events is similar to skeletal muscle 1. Influx of sodium cells get + 2. Depol. moves down ttubules 3. SR releases Ca 4. Ca allows myosinactin interaction 5. Yada-yada Electrocardiogram---ECG or EKG • EKG – Action potentials of all active cells can be detected and recorded • P wave – atrial depolarization • P to Q interval – conduction time from atrial to ventricular excitation • QRS complex – ventricular depolarization • T wave – ventricular repolarization Electrocardiography (EKG) • 3 deflection waves – 1st P wave: atrial depolarization – 2nd QRS complex: Ventricle depol. – 3rd T wave: ventricle repolarization P-Q normal 0.16 sec Q-T normal 0.38 sec Sample EKGs Summary of events during cardiac cycle










![EKG Basics.ppt [Read-Only]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002480056_1-5f04651d7c4aad2eb9878340a342a83b-150x150.png)