* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resistors in Series and Parallel
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Invention of the integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Charlieplexing wikipedia , lookup
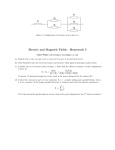
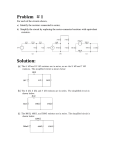
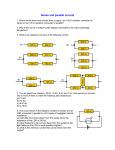
RESISTORS IN SERIES AND PARALLEL Ch. 20 - 2 Resistors : Series In a series circuit, all components are connected endto-end, forming a single path for electrons to flow. When resistors are connected in series, the current in each resistor is the same. Resistors: Series Total current in a series circuit depends on how many resistors are present and how much resistance each offers. The equivalent resistance can be used to find current. Guided Practice Open books to pg. 738 Sample Problem 20A Resistors : Series Series circuits require all elements to conduct. Resistors: Parallel In a parallel circuit, all components are connected across each other, forming exactly two sets of electrically common points. Resistors: Parallel The sum of currents in parallel resistors equals the total current. Resistors in parallel have the same potential differences across them. Resistors: Parallel The equivalent resistance must always be less than the smallest resistance in the group of resistors. Guided Practice Open books to pg. 743 Sample Problem 20B Summary Table pg. 742